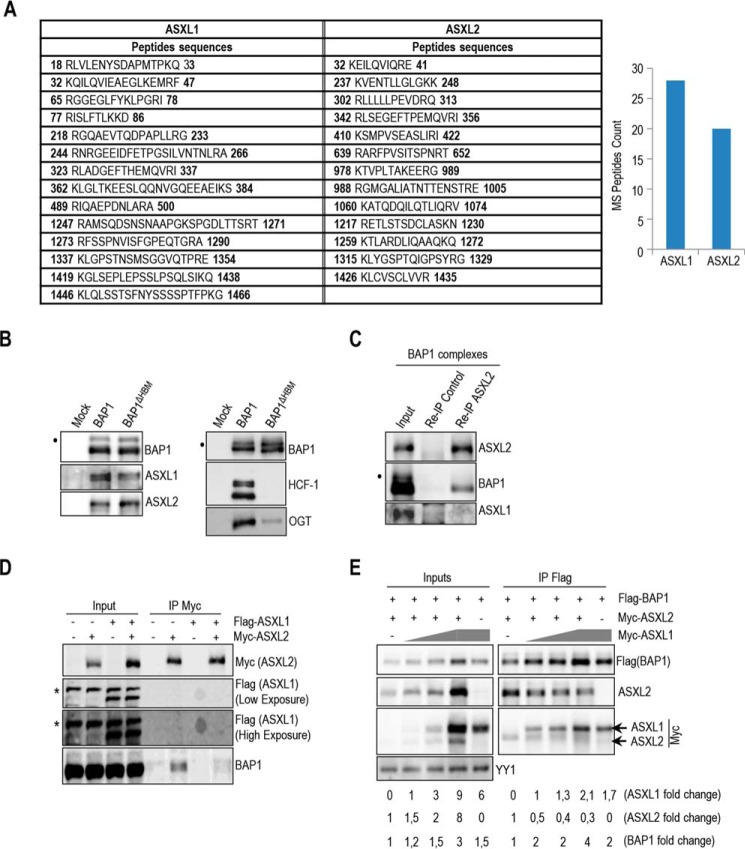
FIGURE 1.
BAP1 interacts with either ASXL1 or ASXL2. A, BAP1 complexes contain relatively similar amounts of ASXL1/2 proteins. ASXL1/2 peptides were identified by mass spectrometry following the purification of BAP1 complexes from HeLa S3 cells. The amino acid positions of the peptides are indicated. B, HCF-1 is not required to maintain the interaction between BAP1 and ASXL1/2. Purification of BAP1 or BAP1ΔHBM (lacking the HCF-1-binding motif) complexes and detection of ASXL1/2 and BAP1 were done by immunoblotting (left panel). The immunopurified proteins were also analyzed by immunoblotting to detect the two major components of the BAP1 complexes, HCF-1 and OGT (right panel). Note that OGT is greatly reduced in the BAP1ΔHBM complexes due to the absence of HCF-1. C, reciprocal immunoprecipitation (Re-IP) of ASXL2 from the purified BAP1 complexes. D, 293T cells were transfected with Myc-ASXL2 (6 μg) with or without FLAG-ASXL1 (4 μg) expression vectors and harvested, 3 days later, for IP of Myc (ASXL2). E, 293T cells were transfected with FLAG-BAP1 (0.1 μg) and Myc-ASXL2 (3 μg) constructs in the presence of increasing amounts of Myc-ASXL1 construct (1, 2, and 5 μg) and harvested, 3 days later, for IP of BAP1 using anti-FLAG. Overexpressed Myc-ASXL2 was detected with anti-ASXL2 and anti-Myc antibodies. ASXL1 was detected with anti-Myc antibody. The difference in molecular weight allows discrimination between ASXL1 and ASXL2 bands. YY1 is used as a loading control. Quantification of band intensity for each protein was conducted relative to the lowest amount of transfected plasmid. The dot and the asterisk indicate a monoubiquitinated form of BAP1 (31) and nonspecific bands, respectively (B–D).