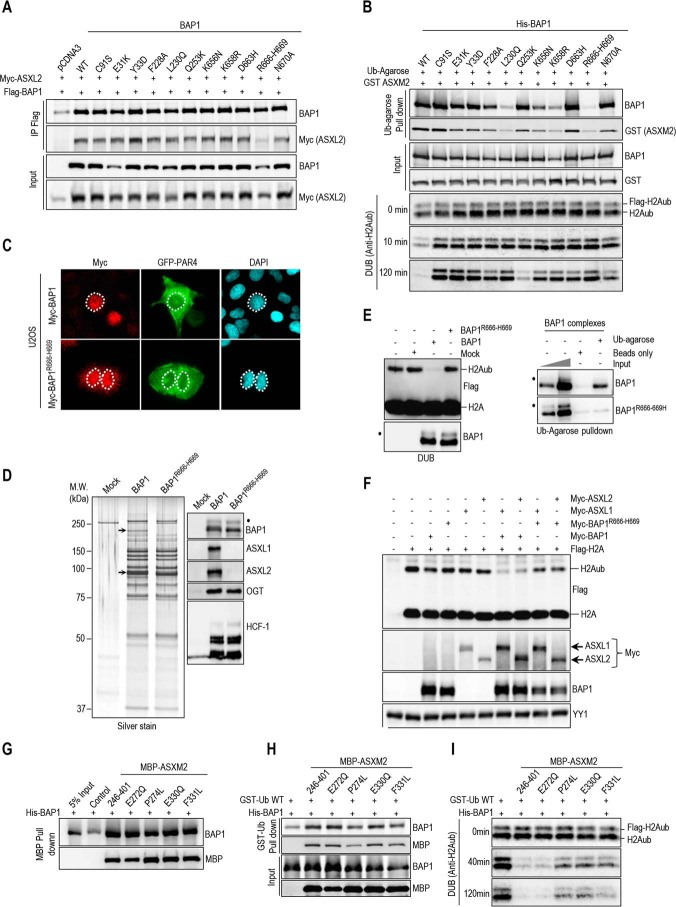
FIGURE 9.
Disruption of BAP1 ubiquitin binding and DUB activity by cancer-associated mutations of BAP1 and ASXL2. A, R666-H669 BAP1 cancer mutation abolishes its interaction with ASXL2. Myc-ASXL2 (6 μg) construct was co-transfected in 293T with either FLAG-BAP1, FLAG-BAP1 C91S, or FLAG-BAP1 mutants constructs (1 μg), and cells were harvested for FLAG IP of BAP1 followed by immunoblotting. B, ubiquitin pulldown assay and in vitro DUB assays of nucleosomal H2A using GST-ASXM2 and His-BAP1, His-BAP1C91S, or the different recombinant mutant forms of BAP1. The same amounts of recombinant proteins as presented in Figs. 5–7 were used for the in vitro reactions. C, U2OS cells were transfected with either Myc-BAP1 (4 μg) or Myc-BAP1 R666-H669 (4 μg) along with GFP-PAR4 (0.5 μg). Three days later, cells were harvested for immunostaining using the indicated antibody. Cells expressing BAP1 or BAP1R666-H669 were encircled. D, BAP1 complexes were purified from HeLa cells stably expressing FLAG-HA-BAP1 or FLAG-HA-BAP1R666-H669. Left panel, silver stain shows the profiles of the complexes. Right panel, Western blot detection of the major components of the BAP1 complexes. The high and low arrows indicate the position of ASXL2 and BAP1, respectively. E, in vitro DUB assay of nucleosomal H2A (top panel) and ubiquitin pulldown assay (bottom panel) using BAP1 and BAP1R666-H669 complexes. F, R666-H669 BAP1 cancer mutation results in the abrogation of its DUB activity in vivo. FLAG-H2A (0.2 μg) construct was co-expressed in 293T cells with either Myc-BAP1 (1 μg) or Myc-BAP1 R666-H669 (1 μg) with or without Myc-ASXL1 (4 μg) or Myc-ASXL2 (6 μg) expression constructs. Three days post-transfection, cells were harvested for immunoblotting. G, His-BAP1 (1.6 μg, 20 nm) and MBP-cancer associated mutants forms of ASXM2 (2 μg, 30 nm) were subjected to MBP pulldown interaction assays. H and I, His-BAP1 and MBP-ASXM2 mutants were subjected as done in Figs. 6–8 to GST-ubiquitin pulldown assay (H) and in vitro DUB assay using nucleosomal H2A (I). The reactions were analyzed by immunoblotting. YY1 is used as a loading control. The dot indicates a monoubiquitinated form of BAP1 (D and E) (31).