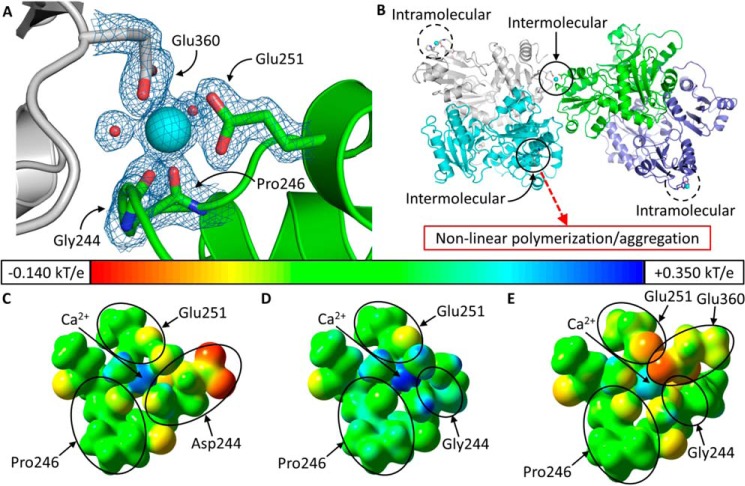
FIGURE 8.
Ca2+ coordination in D244G. A, intermolecular Ca2+ coordination at high affinity site C of D244G. The Ca2+ ion at site C is shown as a large cyan sphere, and the small red spheres are coordinating water molecules. The green protein contains site C, and the gray protein contributes Glu-360 for intermolecular coordination. Blue and red segments in each protein represent nitrogen and oxygen, respectively. The electron density map is contoured at 1.5 σ. B, dimers of D244G have two asymmetrical high affinity site Cs; open circles mark intermolecularly coordinated site Cs, which support non-canonical tetramerization. Thus, site C in the green monomer (whose dimeric partner is in light purple) is complemented by Glu-360 from the gray monomer (whose dimeric partner is in light blue). The dashed circles indicate high affinity site Cs that are coordinated solely intramolecularly. Electrostatic potentials for wild type hCasq1 site C (C), high Ca2+ D244G intramolecular (D), and intermolecular site C (E) are shown. The potential surfaces are shown at an isovalue of 0.200 electron/bohr3. The color scale corresponds to a range of −0.140 (red) to +0.350 kT/e (blue) with green corresponding to a potential of 0.000 kT/e (or −0.200 for red to +0.500 in hartrees for blue where 1 hartree = 627.509 kcal/mol).