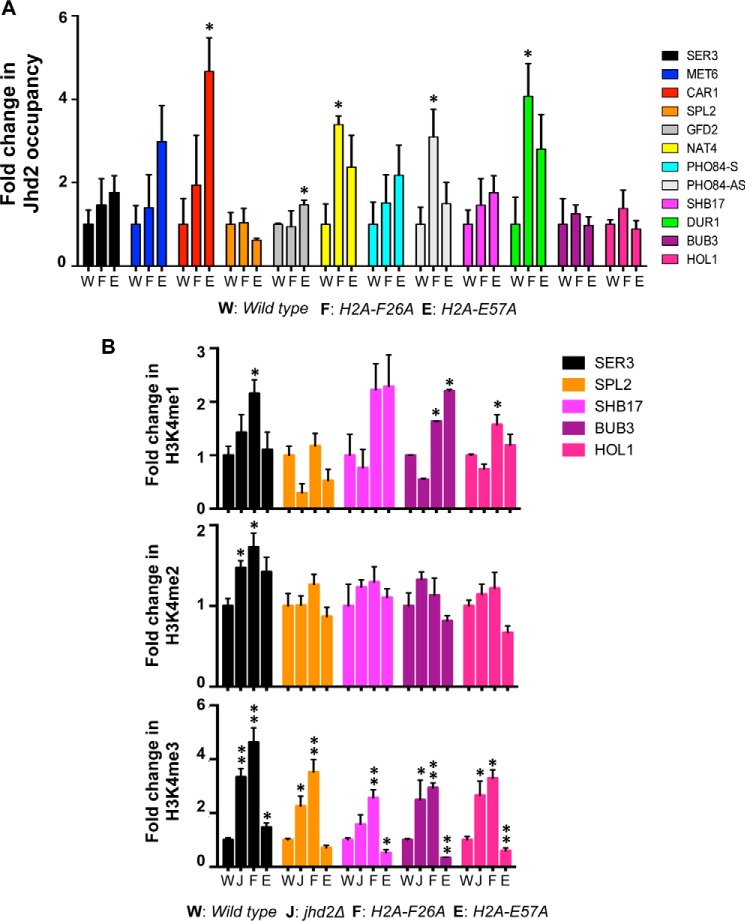
FIGURE 7.
H2A-F26A and H2A-E57A mutations impact chromatin-bound occupancy and H3K4 demethylase functions of Jhd2 at target genes. A, Jhd2-12V5 occupancies at the indicated target genes in control wild-type strain or the two H2A mutants (H2A-F2A or H2A-E57A) were examined by a ChIP assay using α-V5 antibody. Following ChIP and quantitative PCR, the ChIP signal (i.e. V5 immunoprecipitation/input value) obtained from a control strain without V5-tagged Jhd2 (background) was subtracted from the ChIP signal obtained from strains expressing Jhd2-12V5, and the resulting difference was defined as Jhd2 occupancy. The graph shows -fold change in Jhd2 occupancy at a given locus in the H2A-F2A or H2A-E57A mutant relative to Jhd2 occupancy in the control strain, which was set as 1. Error bars, S.E. values obtained from three independent ChIP experiments. Statistical significance was calculated using Student's t test. *, p < 0.05. B, occupancies of H3K4me1, H3K4me2, and H3K4me3 at the indicated target loci in control wild-type H2A, jhd2Δ, H2A-F26A, and H2A-E57A strains were examined with ChIP assays using modification-specific antibodies. ChIP signals for α-H3K4me1, α-H3K4me2, or α-H3K4me3 antibodies obtained in set1Δ strain without any H3K4 methylation were subtracted from the ChIP signal obtained for these antibodies in the four test strains. Background-subtracted ChIP signals for the H3K4 methyl marks were further normalized to the ChIP signal obtained for histone H3, and the resulting value was defined as the H3K4 methyl mark occupancy. -Fold change in the normalized H3K4me1, H3K4me2, or H3K4me3 occupancy in a mutant is shown relative to its occupancy in the control wild-type strain (set as 1). Error bars, S.E. values obtained from three independent ChIP experiments. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.001.