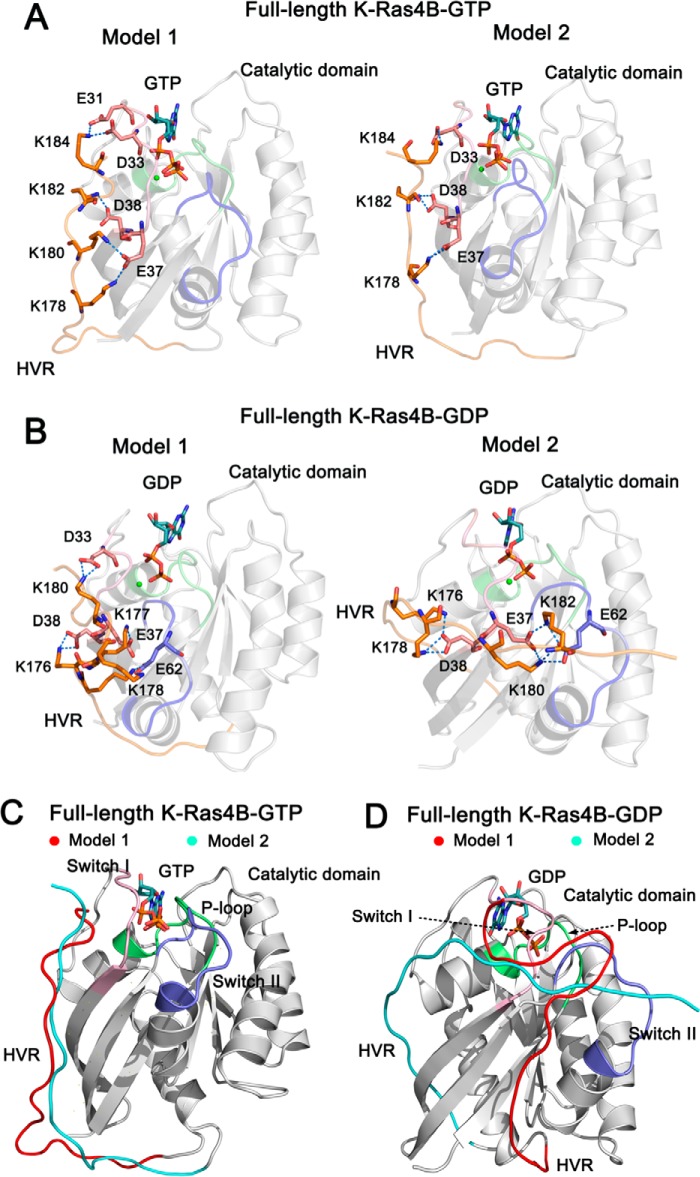
FIGURE 2.
The architectures of full-length GTP-/GDP-bound K-Ras4B. The catalytic domain and the HVR are colored by gray and orange, respectively. The functional P-loop, switch I, and switch II of the catalytic domain are colored lime, pink, and blue, respectively. A, schematic representation of models 1 and 2 of full-length K-Ras4B-GTP. In model 1, the residues Lys-178, Lys-180, Lys-182, and Lys-184 of the HVR form electrostatic interactions with the residues Glu-37, Asp-38, Asp-33, and Glu-31 of the switch I. In model 2, the residues Lys-178, Lys-182, and Lys-184 of the HVR form electrostatic interactions with the residues Glu-37, Asp-38, and Asp-33 of the switch I. B, schematic representation of models 1 and 2 of full-length K-Ras4B-GDP. In model 1 the residues Lys-176, Lys-177, Lys-178, and Lys-180 of the HVR form electrostatic interactions with the residues Glu-37, Asp-38, and Asp-33 of the switch I and Glu62 of the switch II. In model 2 the residues Lys-176, Lys-178, Lys-180, and Lys-182 of the HVR form electrostatic interactions with the residues Glu-37 and Asp-38 of the switch I and Glu62 of the switch II. C, the backbone superimposition of models 1 (HVR colored by red) and 2 (HVR colored by cyan) of full-length K-Ras4B-GTP. The orientation of the HVR with respect to the catalytic domain in the models 1 and 2 is similar. D, the backbone superimposition of models 1 (HVR colored by red) and 2 (HVR colored by cyan) of full-length K-Ras4B-GDP. The orientation of the HVR with respect to the catalytic domain in the models 1 and 2 is markedly different. In model 1, the HVR runs between the β1 strand and the helix α5, whereas in model 2 it runs between the L2 loop and β2 strand.