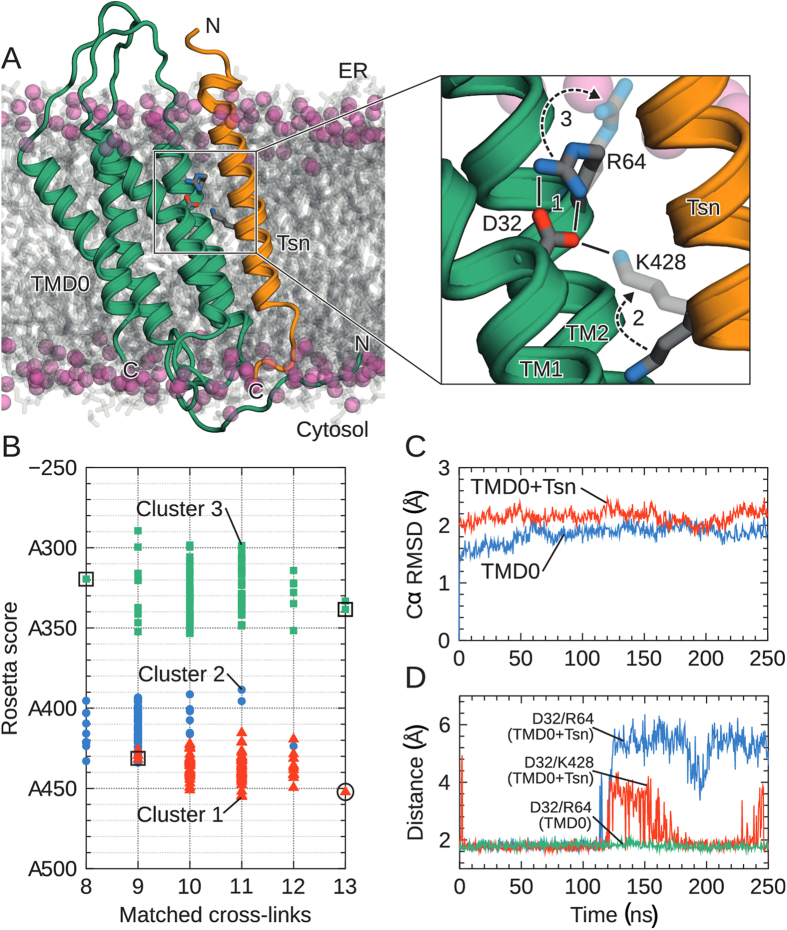
Figure 5. Structure of TMD0TAP1 and tapasin-binding mechanism.
(A) Structure of the TMD0 4-TM bundle associated with the tapasin TM helix (coordinates after 50 ns of MD simulation). Lipid head groups (phosphorus atoms) are shown as spheres; acyl tails are in grey. Water is omitted for clarity. Magnification highlights the ionic lock-switch mechanism: Intra-molecular D32/R64TAP1 ionic lock initially stabilizes charged D32 in the membrane (step 1). Upon tapasin binding, the inter-molecular D32/K428tapasin salt bridge is established (step 2). This promotes rupture of the D32/R64 interaction, with R64 moving towards the lipid head groups (step 3). (B) Rosetta scores of predicted TMD0 structure clusters and their match to the experimental cross-links, where low scores are favorable. The circle indicates the selected final TMD0TAP1 model. Models surrounded by a rectangle were chosen for control simulations (Fig. S4). (C) Cα-RMSD of the TM helices with respect to starting structure during MD. (D) Time series of the salt bridge (minimal residue-residue distance) illustrating the ionic lock-switch mechanism.