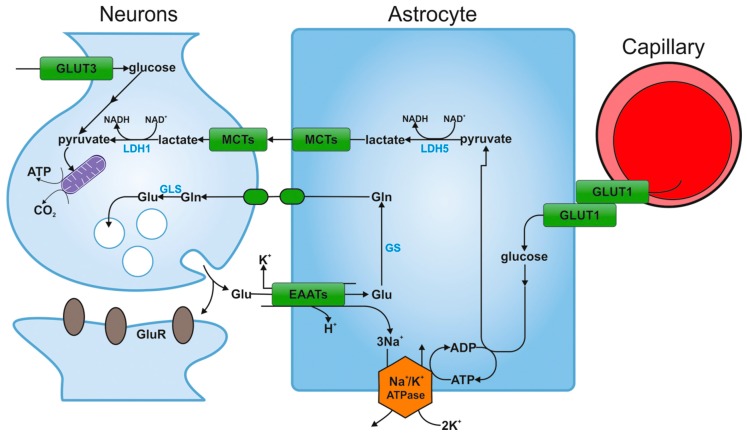
Figure 4.
The hypothesis of astrocyte-neuron lactate shuttle [16]. Glucose is transported from blood vessels to astrocytes by endothelial cells. After entering the astrocyte via GLUT1, part of the glucose is metabolized to lactate via pyruvate by the isoenzyme of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH5). Then lactate is transported outside the astrocyte through the MCT transporter and is captured by neurons, also via the MCT transporter. Intracellular lactate in the neuron is oxidized to pyruvate by the other isoenzyme of lactate hydrogenase (LDH1) and is metabolized along the oxygen pathway. Glucose may be also transported directly into neuronal cells and penetrates into these cells via GLUT3. GLUT1, GLUT3: glucose transporters; MCT: monocarboxylate transporter; TCA: Krebs cycle; GS: glutamine synthetase; Glu: glutamate; Gln: glutamine; GluR: receptor for glutamate; EAATs: excitatory amino-acid transporters; GLS: glutaminase; LDH1, LDH5: isoenzymes of lactate dehydrogenase.