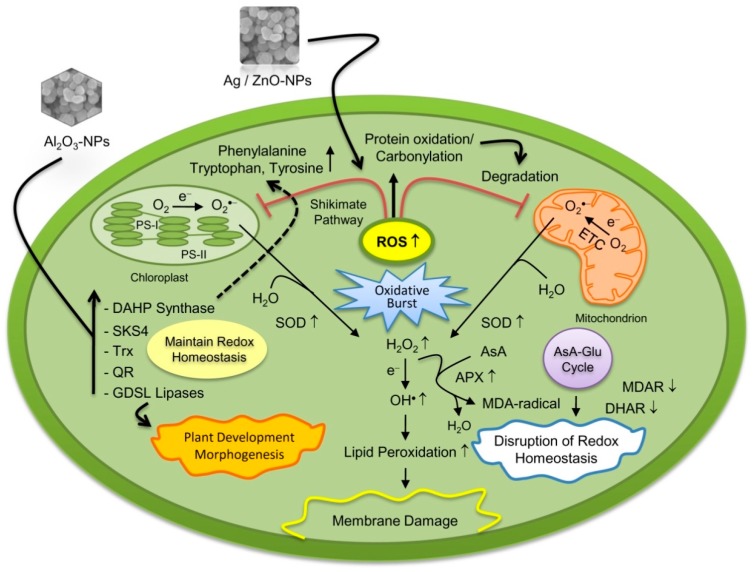
Figure 1.
Cellular toxicity induced by nanoparticles (NPs). Exposure to NPs potentially leads to toxic side effects such as enhanced ROS generation, disruption of redox homeostasis, lipid peroxidation, impaired mitochondrial function, and membrane damage. Upward arrows indicate increased and downward arrows indicate decreased protein abundance in response to NPs stress, respectively. Dotted arrow represents shikimate pathway, a common biosynthetic route for the synthesis of aromatic amino acids. Abbreviations: APX, ascorbate peroxidase; AsA, reduced ascorbate; DAHP, 3-deoxy-D-arabino-heptulosonate-7-phosphate; DHAR, dehydroascorbate reductase; ETC, electron transport chain; H2O2, hydrogen peroxide; MDA, malondialdehyde; MDAR, monodehydroascorbate reductase; PS, photosystem; QR, quinone reductase; ROS, reactive oxygen species; SKS4, SKU5 similar 4 protein; SOD, superoxide dismutase; Trx, thioredoxin.