Fig. 1.
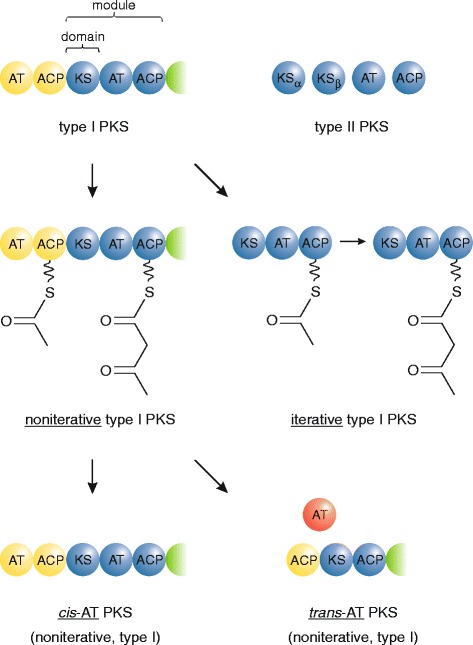
Simplified scheme of PKS subtypes relevant in this work. Type I PKSs (top) are multifunctional proteins, whereas type II PKSs consist of monofunctional proteins that associate into a noncovalent complex. In noniterative type I PKS (middle), which is multimodular, each cycle of elongation and processing is accomplished by one module. In contrast, iterative type I PKS are typically unimodular, and this module is used multiple times during the biosynthesis of a single polyketide. Noniterative type I PKS can have integrated (cis) or free-standing (trans) AT domains (bottom), whereas basically all iterative type I PKSs feature cis-AT domains. See Fig. 2 for domain abbreviations
