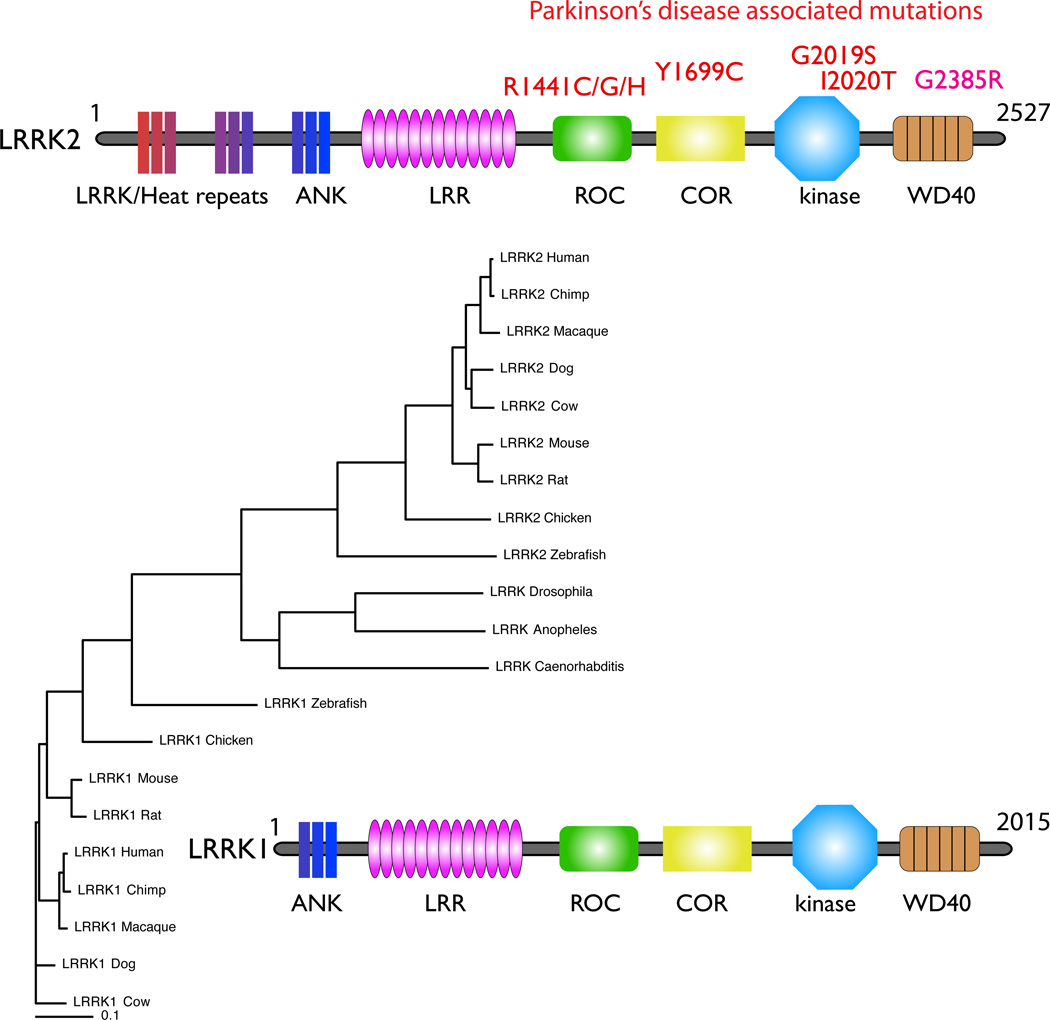
Figure 3. The LRRK family.
Like the synucleins, there are at least two distinct branches of the LRRK family represented by LRRK1 (lower part of the tree) and LRRK2 (upper part of the tree) in vertebrate species. The invertebrate LRRKs form a group that sits between the two vertebrate LRRK homologues (see text). The distinction between the LRRK1 and LRRK2 orthologues includes differences at the N-terminal, where LRRK2 (upper ideogram) includes a series of repeat sequences that LRRK1 (lower ideogram) lacks. Other domains include the anykrin-like repeats (ANK), leucine-rich repeats (LRR), Ras of complex proteins (Roc) and C-terminal of ROC (COR), kinase and WD40 domains.