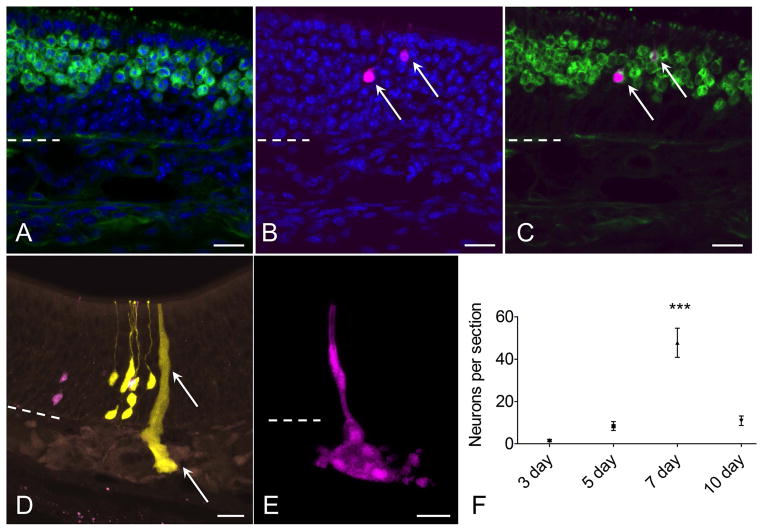
Figure 4.
Characterization of neurons and glands derived from c-Kit+ cells. (A–C) RFP+ (magenta) c-Kit-derived neuron phenotype is confirmed by co-labeling with antibody to olfactory marker protein (OMP, green, arrows). (D, E) Bowman’s glands and ducts also arise from c-Kit+ cells. In a section from a mouse given high-dose tamoxifen, RFP+ and YFP+ neurons are evident, along with a YFP+ gland and duct (arrow). Although these overlapping cells cannot be considered clonally related, the image demonstrates XFP reporter expression in glands, ducts and neurons. (E) From a low-dose TAM-treated mouse, an entire gland and duct RFP+ clone can be visualized from a 60 μm thick z-stack image. (F) Quantification of neurons per section indicates that neuron production from c-Kit+ globose basal cells is highest in mice given TAM at day 7 post lesion (P<0.001, ANOVA, n=3 mice per time point). Dashed line marks basal lamina. Bar = 20 μm in (A–E).