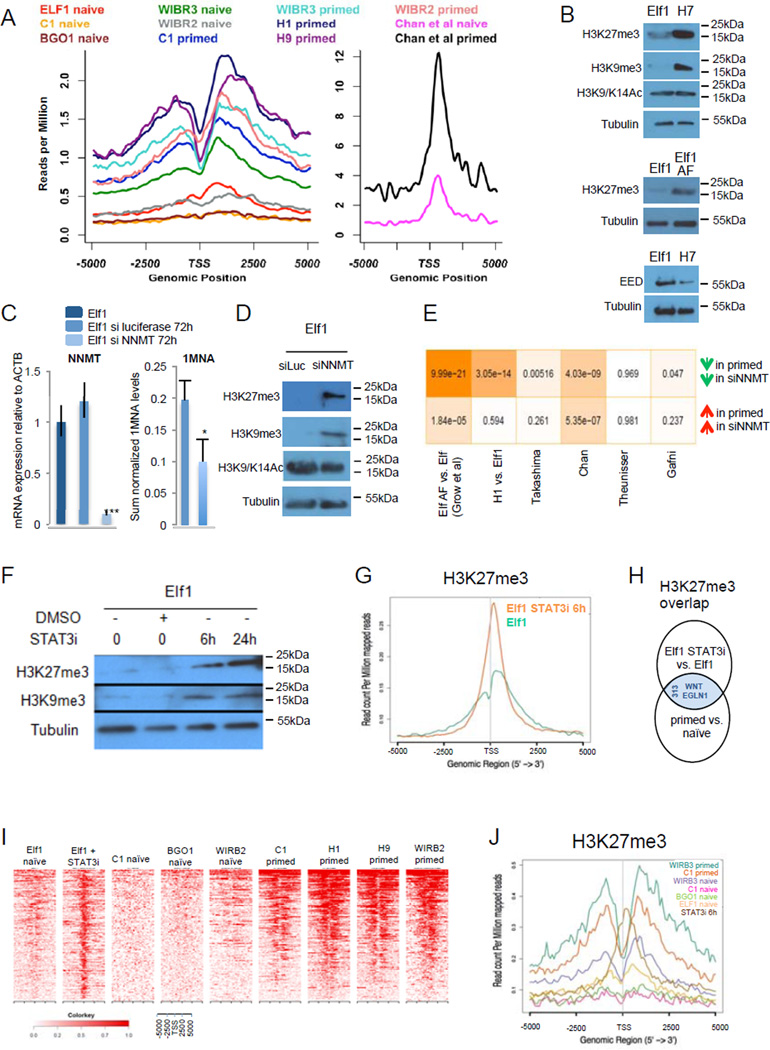
Figure 5. High NNMT expression in naïve hESCs regulates histone methylation status.
A: H3K27me3 reads mapped 5kb around transcription start sites (TSS) of 648 developmental genes were plotted for Ware et al., Gafni et al., Theunissen et al., Bernstein et al. (left panel) and Chan et al (right panel) ChIP-seq data sets. B: Western blot analyses show higher H3K27me3 and H3K9me3 in primed hESCs (H7, Elf1 AF) than naïve hESCs (Elf1). C: qPCR analysis shows a knock-down regulation of NNMT using siRNA (50 nM, 72h) in naïve hESCs (Elf1), inducing a decrease of 1-MNA levels (qPCR n=3; s.e.m., p=0.001, 2-tailed t-test; HILIC n=4, s.e.m., p=0.039 1-tailed t-test) D: Western blot analysis of histone marks in Elf1 cells treated with siRNA against NNMT or siRNA against luciferase as a control. E: Hypergeometric test p-values for the overlap between genes expressed higher (lower) in siNNMT compared to siLUC and genes expressed higher (lower) in primed lines compared to naïve lines from multiple studies. Color shade is proportional to negative log10 of p-values. siLUC transcriptomic signature has significant overlap with the ELFAF vs. Elf1 data set. F: Western blot analysis of histone modifications after treatment of Elf1 cells with 100 µM of STAT3 inhibitor. G: 6h treatment with STAT3 inhibitor (100 µM) in Elf1 cells increases H3K27me3 marks, as shown by ChipSeq analysis on all genes. H: WNT ligands and EGLN1 are among the 313 overlapping genes with increased H3K27me3 mark in primed vs. naïve hESCs (8,10,64), and Elf1 cells treated for 6h with 100uM STAT3 inhibitor vs. Elf1 cells. I: Windowed chromatin heatmaps of H3K27me3 profile +/− 5kb of promoters of the 313 overlapping genes with increased H3K27me3. J: H3K27me3 reads from ChIP-seq data mapped 5kb around TSS were plotted for naïve hESCs (C1, WIBR3, BGO18, and Elf112.), primed hESCs (C1, WIBR38, H112) and naïve hESCs Elf1 treated for 6h with 100µM of STAT3 inhibitor. Unprocessed original scans of blots are shown in Supplementary Fig.9. For raw data, see Supplementary Table 4. n= number of biological replicates.