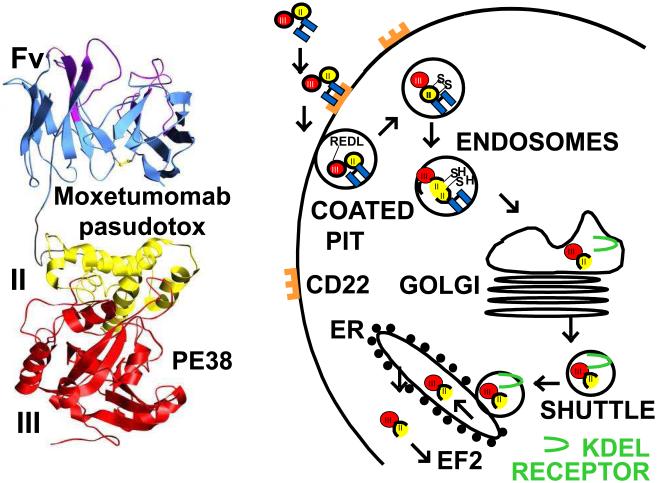
Figure 2. Structure and intoxication of moxetumomab pasudotox.
Left, ribbon diagram of moxetumomab pasudotox showing the Fv and domains II and III of Pseudomonas exotoxin. On the right are steps required for the entry and cell killing. After internalization, the truncated 38 kDa toxin fragment PE38 undergoes proteolysis and disulfide-bond reduction to separate the catalytic domain III from the ligand [48-50]. The carboxy terminal lysine residue is removed [79] resulting in a 35 kDa carboxy terminal toxin ending in REDL. The KDEL receptor transports this fragment from the Golgi to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) [52], where it translocates to the cytosol, ADP-ribosylates elongation factor 2 [41], and leads to apoptotic cell death [56].