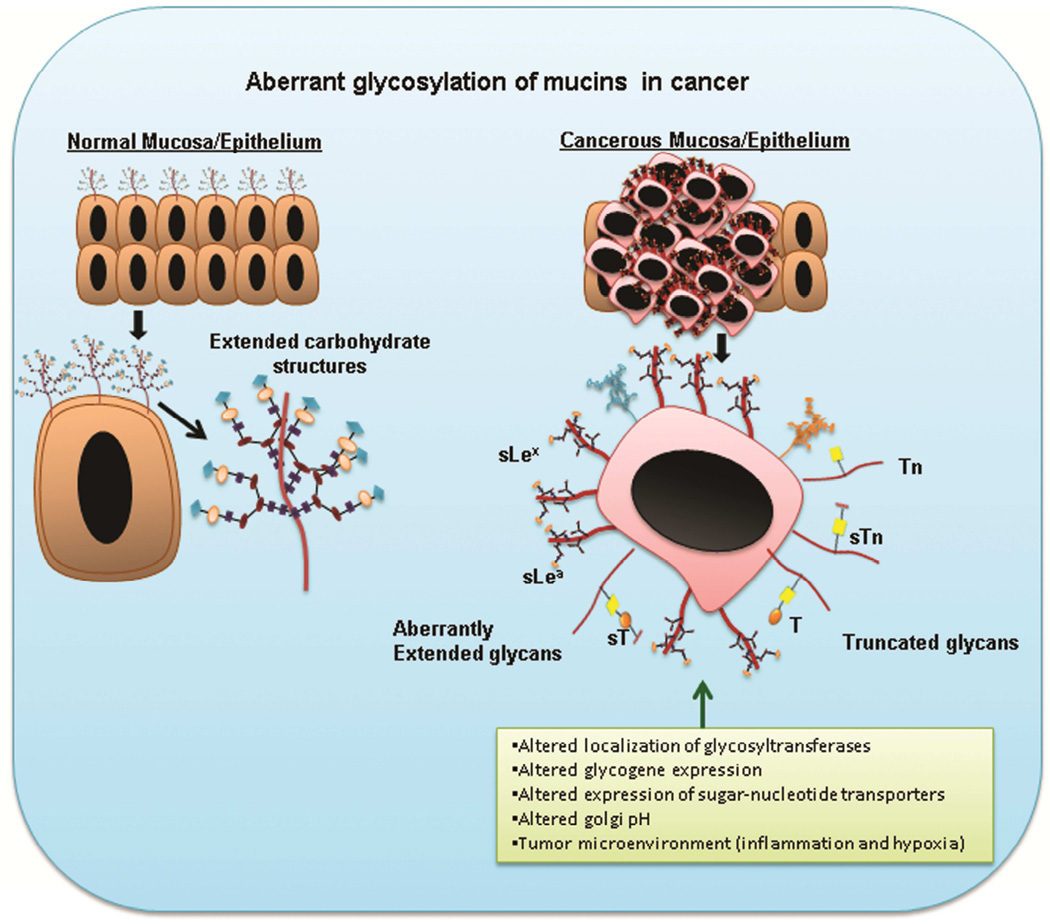
Figure 3. Aberrant glycosylation of mucins during cancerous conditions.
Differential glycosylation of mucins occur in malignant conditions that result in truncated glycan structures such as Tn, STn, and T, and several Core 2 extended structures such as sLex and sLea. This aberrant glycosylation is a result of several factors such as altered glycogene expression, mislocalization of glycosyltransferases, abnormal Golgi pH, and the tumor microenvironment.