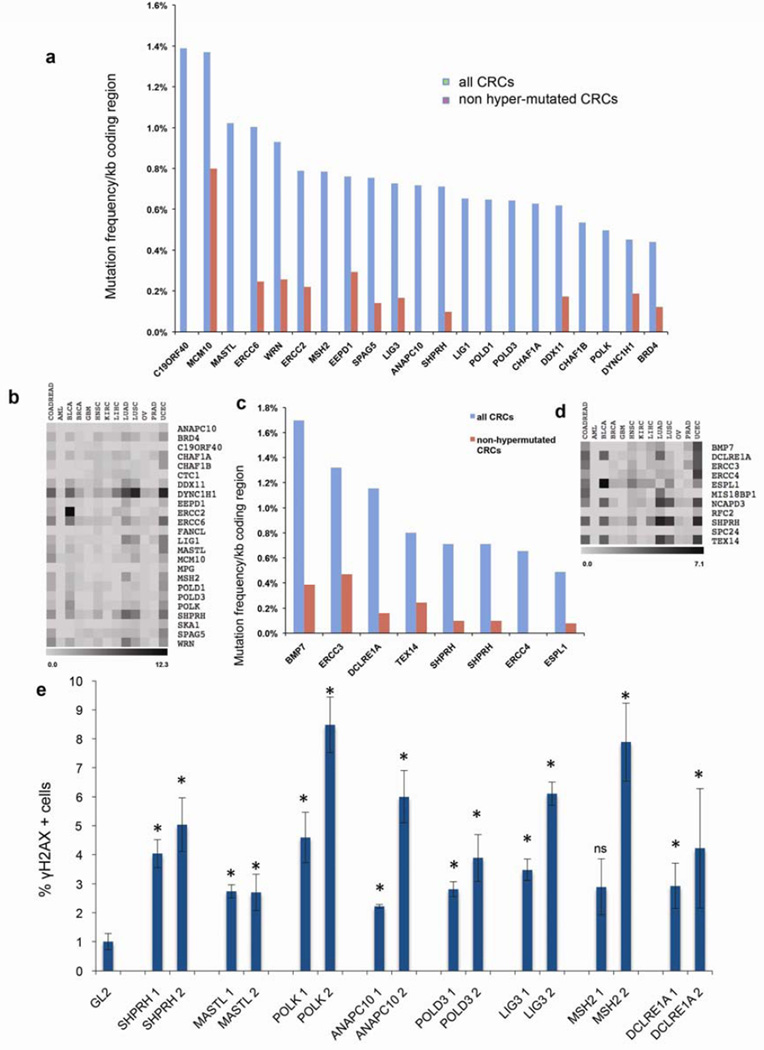
Figure 3. Some variant Genes are mutated in sCRC and suppress DSBs in CRC cells.
(a) TCGA CRC somatic mutation frequencies in genes that exhibited HQVs in the UFCRC patients (a) or polyposis patients (c), normalized to coding region length (in kb). Abbreviations (cBioportal): COADREAD, Colorectal Adenocarcinoma; AML, Acute Myeloid Leukemia; BLCA, Bladder Urothelial Carcinoma; BRCA, Breast Carcinoma; GBM, Glioblastoma Multiforme; HNSC, Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma; KIRC, Kidney Renal Clear Cell Carcinoma; LIHC, Liver Hepatocellular Carcinoma; UAD, Lung Adenocarcinoma; LUSC, Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma; OV, Ovarian Serous Cystadenocarcinoma; PRAD, Prostate Adenocarcinoma; UCEC, Uterine Carcinoma. (b) ‘Heat map’ of somatic mutation frequencies in the gene sets from (a), in several major tumor types. Grayscale ranges from white (no mutations) to black (the highest possible number, as indicated, expressed in %) (c, d) Same analysis as for (a, b), performed for polyposis patients. (e) siRNA depletion of genes identified as variant in UFCRC and polyposis patients elevates γH2AX in HCT116 cells. Cells were transfected with the designated siRNAs (two per gene) and scored for γH2AX. *, P < 0.05 versus GL2; ns, not significant.