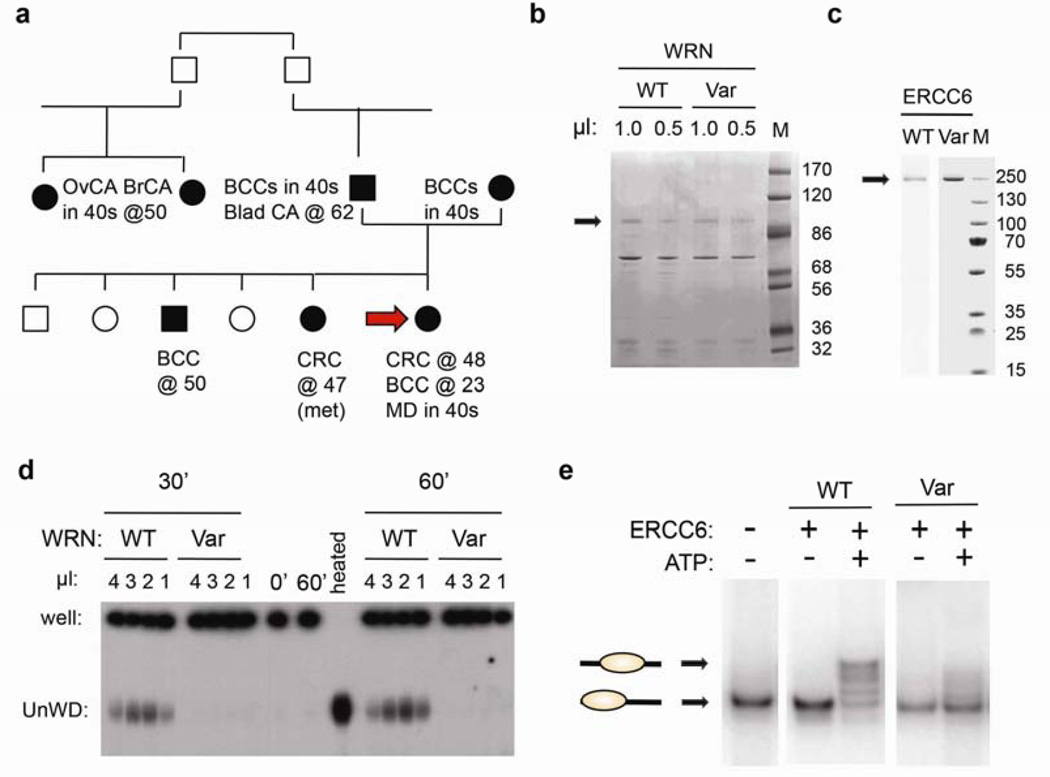
Figure 4. Variants of WRN and ERCC6 identified in Pt1 exhibit defective enzymatic activity.
(a) Pt1 pedigree with ages of diagnosis. Carcinomas: basal cell: BCC, bladder: Blad CA, ovarian: OvCA, breast: BrCA. Macular degeneration: MD. Arrow: Pt1. (b) Comparable preparations of recombinant wild type (WT) and variant (Var) Xenopus WRN helicase domains (assessed by Coomassie blue staining of the designated extract volumes. M: molecular weight markers, in KD. (c) Defective helicase activity of the WRN T705I variant. Persistently basepaired DNA remains in the well, while unwound (UnWD) oligonucleotide migrates into the gel. (−) controls: No added helicase (0’ or 60’), (+) control: heat denaturation of DNA (heated). Similar results were seen in three independent experiments using two independent preparations. (d) Comparable preparations of recombinant wild type (WT) and variant (Var) ERCC6 helicase domains, as in (b). (e) ERCC6 N180Y variant is defective in chromatin remodeling. End positioned nucleosomes with a single 91-bp DNA overhang (lower band) used as substrate. WT ERCC6 generated nucleosomes at different translational positions in an ATP-dependent manner (upper bands). Similar results were seen in three independent experiments.