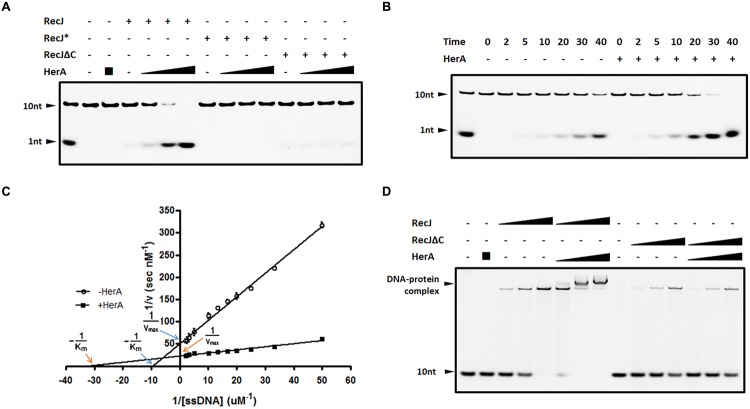
FIGURE 4.
DrHerA enhanced DrRecJ nuclease activity and ssDNA binding ability. (A) DrHerA enhanced DrRecJ nuclease activity. Hundred nanomolar 10 nt ssDNA was used as substrate for RecJ digestion. DrRecJ ssDNA nuclease activity was analyzed in the absence or presence of DrHerA in various molar ratios (RecJ monomer: HerA hexamer = 1:1, 1:4, 1:16). RecJ∗ represented the inactive DrRecJ protein DrRecJ (D158A/H159A/H160A). Five nanomolar DrRecJ was used while 40 nM DrRecJΔC was used in the reaction system. (B) Time course experiments for DrHerA enhancement on DrRecJ nuclease activity. DNA hydrolysis by DrRecJ in the presence or absence of DrHerA was analyzed at different time points (2, 5, 10, 20, 30, and 40 min). (C) Steady-state kinetics analyses of DNA hydrolysis by DrRecJ in the presence or absence of DrHerA. The amount of undegraded substrate remaining for each concentration was quantitated and used to calculate the velocity (v) of the reaction, the reciprocal of which was plotted against the reciprocal of substrate concentration (1/[v] versus 1/[S]). Lineweaver–Burk equation was used for the calculation of kinetic parameters. Error bars indicate standard deviation. (D) DrHerA enhanced DrRecJ ssDNA binding activity. Hundred nanomolar 10 nt ssDNA was used as substrate for RecJ binding. The molar ratio: DNA: DrRecJ = 1:1, 1:2, 1:4; DNA: DrRecJΔC = 1:4, 1:8, 1:16; HerA (hexamer): DrRecJ (or DrRecJΔC) = 8: 1.