Figure 11.
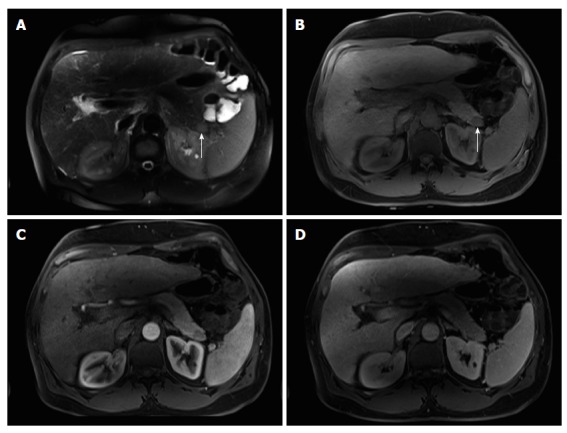
Intra-pancreatic splenule. Axial T2-weighted SS-ETSE (A), pre-contrast fat-suppressed T1-weighted (B) GRE and post-gadolinium fat-suppressed T1-weighted GRE images acquired in the arterial (C) and venous (D) phases of enhancement. There is a well-marginated and lobulated round intra-pancreatic splenule (arrows, A and B) that shows isointense signal to the pancreas on T2- and T1-weighted images (A and B). This nodule is hypointense compared to the background pancreas on the precontrast T1-weighted image (B) and demonstrates lesser enhancement relative to the pancreas on the arterial phase (C) and hepatic venous phase (D). The enhancement pattern was homogenous on the postgadolinium images and similar to that of the pancreas. SS-ETSE: Single-shot echo train spin echo; GRE: Gradient echo.
