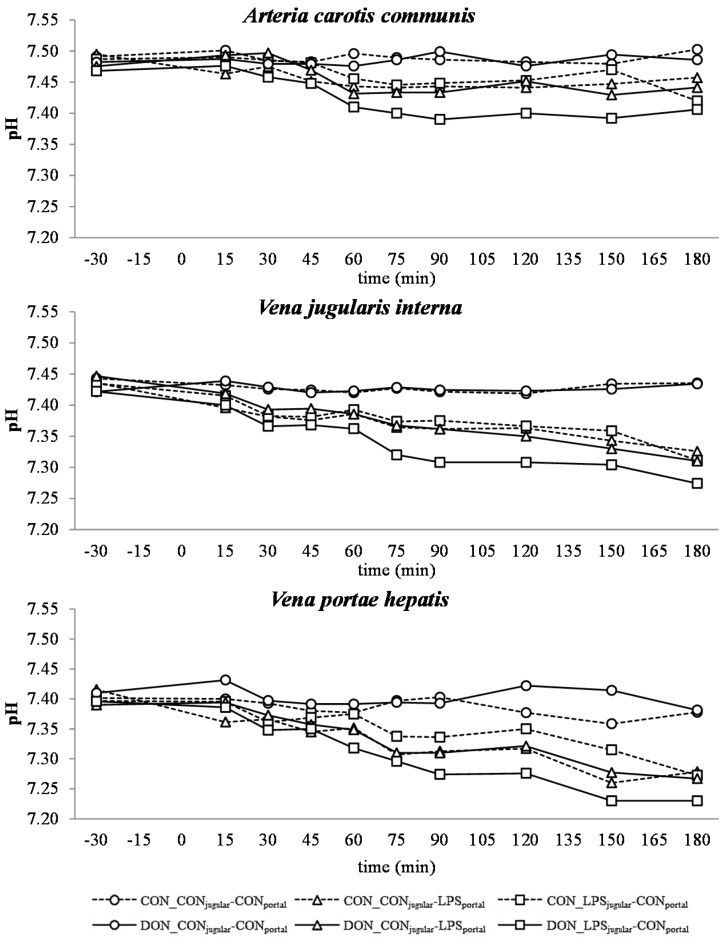
Figure 4.
Effect of chronic enteral Fusarium toxin deoxynivalenol (DON) exposure and pre- or post-hepatic E. coli lipopolysaccharide (LPS) infusion on arterial, jugular or portal blood pH in pigs. Reference value: 7.42 in arterial blood [26]. Barrows were either fed a DON contaminated ration (4.59 mg/kg feed) or control feed during 29 days. Infusion groups were divided as follows: pre-hepatic LPS infusion (CON_CONjugular-LPSportal, n = 7 and DON_CONjugular-LPSportal, n = 6), post-hepatic LPS infusion (CON_LPSjugular-CONportal, n = 8 and DON_LPSjugular-CONportal, n = 6), and control infusion (CON_CONjugular-CONportal, n = 7 and DON_CONjugular-CONportal, n = 7). Infusion from time 0 until 60 min with 7.5 µg LPS/kg BW in 0.9% saline. Feed was offered during 15 min prior to infusion start. LSMeans. PSEM = 0.02. Significance: Group (G): p ≤ 0.001; Catheter (C): p ≤ 0.001; Time (T): p ≤ 0.001; G × C × T: p ≤ 0.001. Table illustrates differences between DON and CON fed post-hepatic LPS infused groups at different times. T = trend (p ≤ 0.10).
| post hoc test (p-value) CON_LPS-CON vs. DON_LPS-CON | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| time (min) | −30 | 15 | 30 | 45 | 60 | 75 | 90 | 120 | 150 | 180 |
| A. carotis | 0.499 | 0.611 | 0.327 | 0.236 | 0.105 | 0.105 | 0.038 | 0.061 T | 0.006 | 0.623 |
| V. jugularis | 0.636 | 0.585 | 0.548 | 0.630 | 0.268 | 0.051 T | 0.015 | 0.035 | 0.047 | 0.176 |
| V. portae | 0.975 | 0.736 | 0.637 | 0.495 | 0.039 | 0.132 | 0.024 | 0.007 | 0.002 | 0.129 |