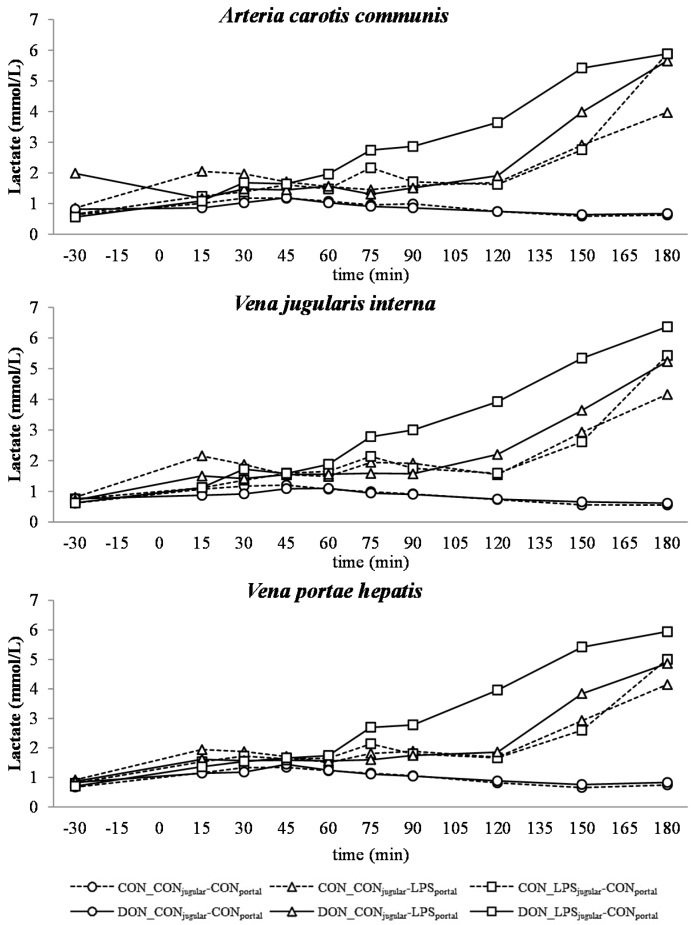
Figure 5.
Effect of chronic enteral Fusarium toxin deoxynivalenol (DON) exposure and pre- or post-hepatic E. coli lipopolysaccharide (LPS) infusion on arterial, jugular or portal blood lactate in pigs. Reference: 0.84 ± 0.24 mmol/L in venous blood [28]. Barrows were either fed a DON contaminated ration (4.59 mg/kg feed) or control feed during 29 days. Infusion groups were divided as follows: pre-hepatic LPS infusion (CON_CONjugular-LPSportal, n = 7 and DON_CONjugular-LPSportal, n = 6), post-hepatic LPS infusion (CON_LPSjugular-CONportal, n = 8 and DON_LPSjugular-CONportal, n = 6), and control infusion (CON_CONjugular-CONportal, n = 7 and DON_CONjugular-CONportal, n = 7). Infusion from time 0 until 60 min with 7.5 µg LPS/kg BW in 0.9% saline. Feed was offered during 15 min prior to infusion start. LSMeans. PSEM = 0.56. Significance: Group (G): p ≤ 0.001; Catheter (C): p = 0.78; Time (T): p ≤ 0.001; G × C × T: p ≤ 0.001. Table illustrates differences between DON and CON fed post-hepatic LPS infused groups at different times. T = trend (p ≤ 0.10).
| post hoc test (p-value) CON_LPS-CON vs. DON_LPS-CON | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| time (min) | −30 | 15 | 30 | 45 | 60 | 75 | 90 | 120 | 150 | 180 |
| A.carotis | 0.912 | 0.845 | 0.714 | 0.969 | 0.558 | 0.484 | 0.161 | 0.014 | 0.001 | 0.999 |
| V.jugularis | 0.871 | 0.993 | 0.656 | 0.993 | 0.775 | 0.424 | 0.120 | 0.004 | 0.001 | 0.245 |
| V.portae | 0.904 | 0.838 | 0.824 | 0.965 | 0.911 | 0.484 | 0.223 | 0.004 | <0.001 | 0.252 |