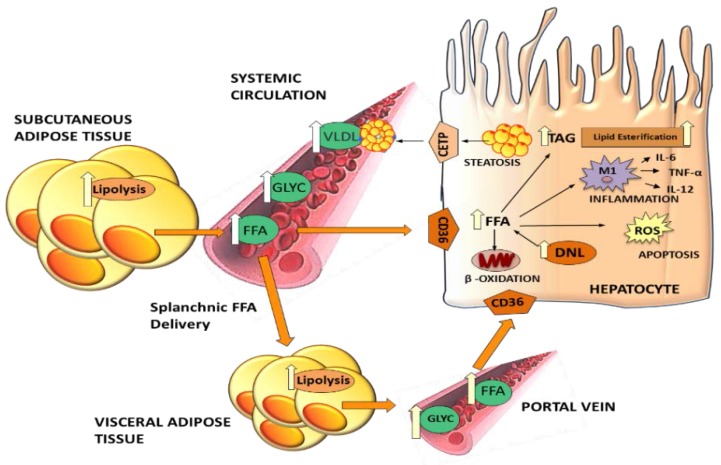
Figure 2.
Effects of increased lipolysis on liver dysfunction. Excess lipolysis results in high free fatty acid (FFA) flux into the liver, where FFAs cause steatosis and exert lipotoxic effects. Triglycerides (TAG) synthetized in the liver are secreted into the plasma circulation as very low density lipoproteins (VLDL) causing dyslipidemia. Visceral fat has a preferential role in hepatic fat accumulation since released FFA reach the liver via the portal vein. Also increased hepatic de novo lipogenesis (DNL), inflammation and oxidative stress contribute to liver damage and hepatocyte dysfunction.