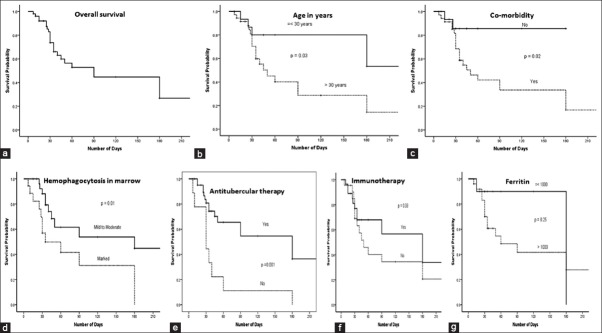
Figure 1.
(Survival patterns in patients with tuberculosis associated hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (TB-HLH) in relation to different parameters by Kaplan-Meier analysis using log-rank test. (a) Overall survival in patients with TB-HLH was approximately 45% after 3 months. On univariate analysis, (b) age > 30 years (P = 0.03); (c) presence of co-morbidity (P = 0.02); (d) evidence of moderate to marked degree of bone marrow hemophagocytosis (P = 0.01); and (e) non usage/delayed usage of antitubercular therapy (P = 0.001) were significantly associated with decreased survival. Usage of immunomodulators and/or immunosuppressive drugs (f) did not contribute significantly (P = 0.33) to the improved survival. High ferritin (>1000 ng/ml) was associated with poor survival; though it was not statistically significant (P = 0.25) (g)d