Figure 8.
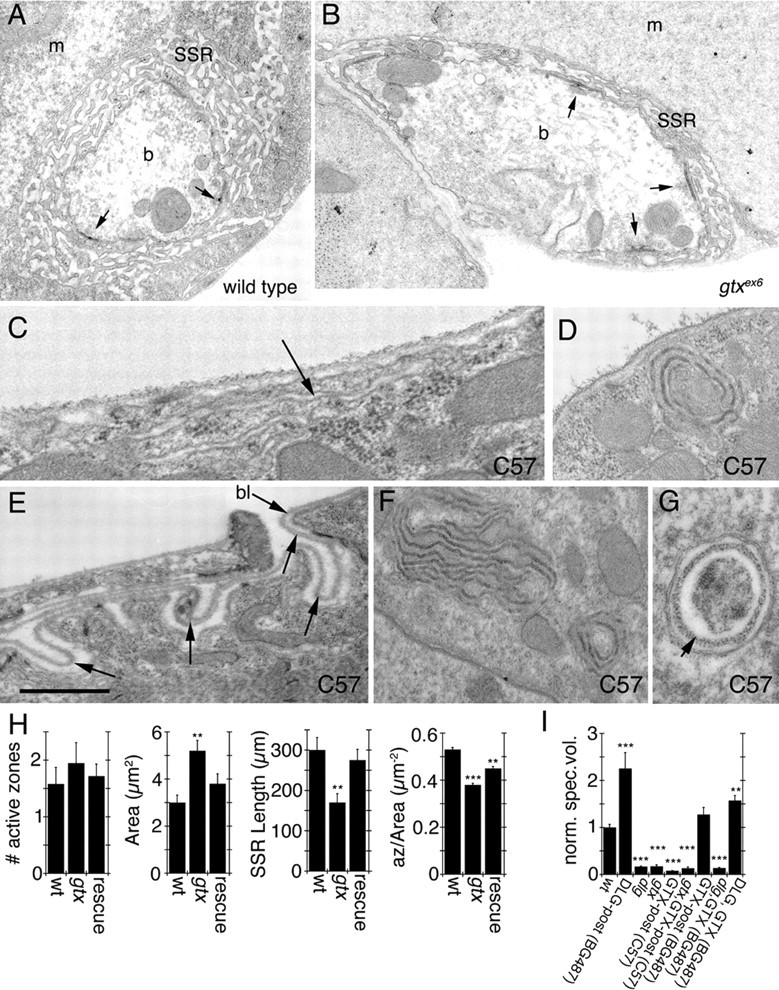
Ultrastructure of synaptic boutons and muscles in gtx mutants. A–G, Electron micrographs of type Ib synaptic boutons (A, B) in wild type (A) and gtx ex6 mutants (B). m, Muscle; b, bouton. Arrows point to T-bar active zones. C–G, Extrasynaptic membrane structures observed in larvae overexpressing GTX using the strong pan-muscle Gal4 driver C57. Arrows in C and E point to surface membranous structures resembling the SSR, and the arrow in G points to electron dense material resembling basal lamina (bl). H, Morphometric analysis of synaptic boutons in wild type, gtx ex6 mutants, and gtx ex6 mutants expressing transgenic GTX using the Gal4 strain BG487. Numbers analyzed were 12 boutons in two wild-type larvae, 19 boutons in two gtx ex6, and 12 boutons in three gtx ex6 expressing GTX in muscles using the BG487 Gal4. I, Quantification of the volume occupied by Spectrin at the postsynaptic area in different genotypes. n = 6 samples for each phenotype; **p = 0.001; ***p < 0.0001. n = 6 for gtx ex6 and gtx ex6; C57 and 8 for all other genotypes. Scale bar: A, B, 1.5 μm; C, 0.2 μm; D, F, 0.5 μm; E, G, 0.3.
