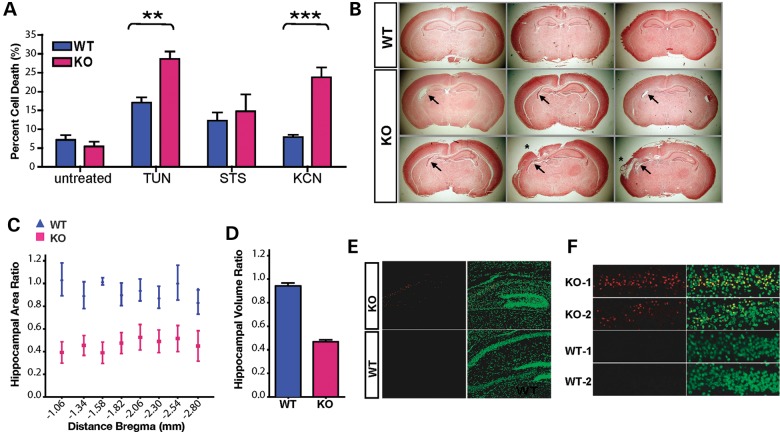
Figure 3.
Plp2 deficiency leads to increased neuronal death in response to ER stress and hypoxia. (A) WT and KO primary cortical neurons were treated with TUN (10 µg/ml) or STS (0.02 µM) for 48 h, or KCN (5 µM/2-deoxy-glucose) for 1 h followed by recovery in regular medium for 24 h. Data are shown as mean ± SEM, n = 6, **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001. (B–F) Neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury model. (B) Coronal sections were stained with trichrome. Representative images are shown here, each picture is from an individual mouse. The left side of the image corresponds to the right side of the brain ipsi-lateral to the ligated CCA. (C) The hippocampal area was measured at eight consecutive levels at 400 µm distance and expressed as the area of the ipsi-lateral hippocampus/contra-lateral hippocampus. The x-axis is the distance from bregma (mm) according to a standard mouse brain atlas. Data are shown as mean ± SEM, n = 12 in each group. (D) Relative volumes of ipsi-/contra-lateral hippocampal area are calculated from the relative area and the distance between each measured areas. Data are shown as mean ± SEM, n = 12 in each group, P = 0.0002. (E) Sections, containing maximum hippocampus area, were stained with TUNEL staining (red). Nuclei were counter stained with Sytox green. Representative images of the hippocampi ipsi-lateral to the CCA ligation are shown here. (F) Enlarged TUNEL staining of the ipsi-lateral CA1 region of two mice from each genotype.