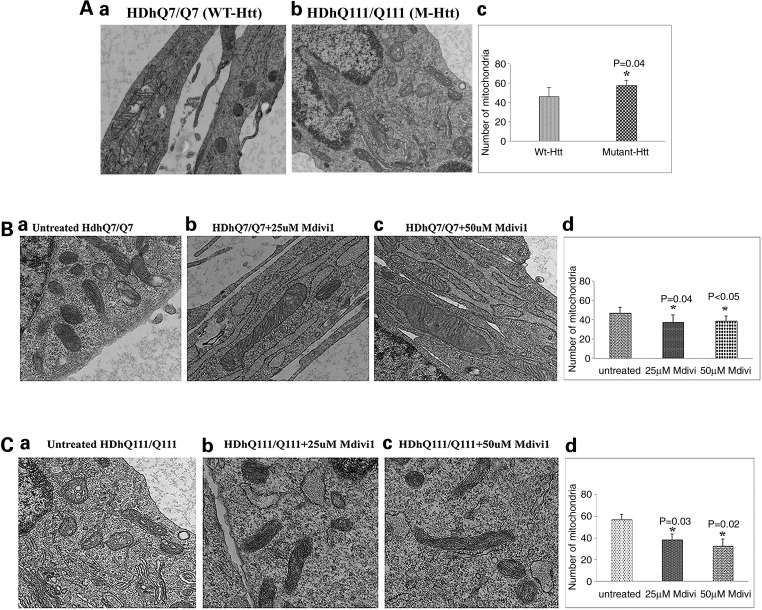
Figure 6.
Transmission electron microscopy of studies. (A) Mitochondrial number between WT Htt and mutant Htt neurons. (a) Healthy, intact mitochondria in the WT Htt neurons; (b) fragmented mitochondria in mutant Htt neurons. (c) Results from quantitative analysis of mitochondria. Significantly increased numbers of mitochondria were found in the mutant Htt neurons (P = 0.04) relative to WT Htt neurons. (B) Transmission electron microscopy of Mdivil-treated and untreated WT Htt neurons. (a) Healthy, intact mitochondria in the WT Htt neurons; (b) healthy, intact and elongated mitochondria in the 25 μm Mdivi1-treated WT Htt neurons. (c) Healthy, intact mitochondria in the 50 μm Mdivi1-treated WT Htt neurons. (d) Results from quantitative analysis of mitochondria. Significantly decreased numbers of mitochondria were found in the WT neurons treated with Mdivil at 25 μm (P = 0.04) and 50 μm (P = 0.04) concentrations compared with the mitochondria in mutant Htt neurons untreated with Mdivi1. (C) Transmission electron microscopy of Mdivil-treated and untreated mutant Htt neurons. (a) Fragmented and structurally damaged mitochondria in the mutant Htt neurons; (b) intact mitochondria in the 25 μm Mdivi1-treated WT Htt neurons. (c) Intact mitochondria in the 50 μm Mdivi1-treated mutant Htt neurons. (d) Results from quantitative analysis of mitochondria. Significantly decreased numbers of mitochondria were found in the mutant neurons treated with Mdivil at 25 μm (P = 0.03) and 50 μm (P = 0.02) concentrations compared with the mitochondria in mutant Htt neurons untreated with Mdivi1.