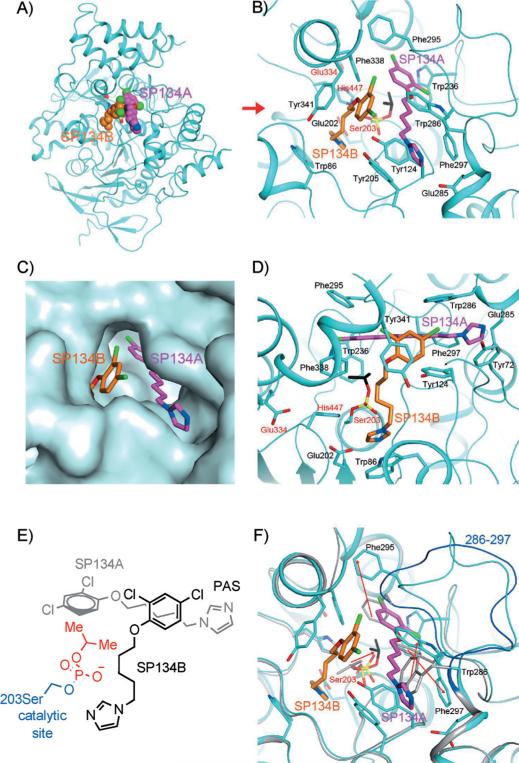
Figure 4.
Interactions between SP134 (15) and AChE. A) Schematic drawing of the overall structure of murine AChE in complex with 15. The two molecules of 15 in each active site are shown as sphere models in magenta (SP134A) and orange (SP134B) for carbon atoms. B) Detailed interactions between 15 and murine AChE. Residues in the catalytic triad are labeled in red. C) Molecular surface showing the binding of the two molecules of 15 in a deep pocket of AChE. D) Detailed interactions between 15 and murine AChE, viewed along the red arrow of panel B). E) Chemdraw schematic representation of interacting 15 molecules from the same perspective as in C). F) Overlay of the structures of the 15 complex (in cyan) and the “aged” DFP (2) adduct (in gray). A large conformational change for residues 286–297 is visible, and the backbone of these residues in the 2 adduct is shown in blue. The red arrows indicate changes in the positions of the side chains that are important for SP134A binding, as well as a rotation of the remaining isopropyl group of 2 to interact with SP134A.