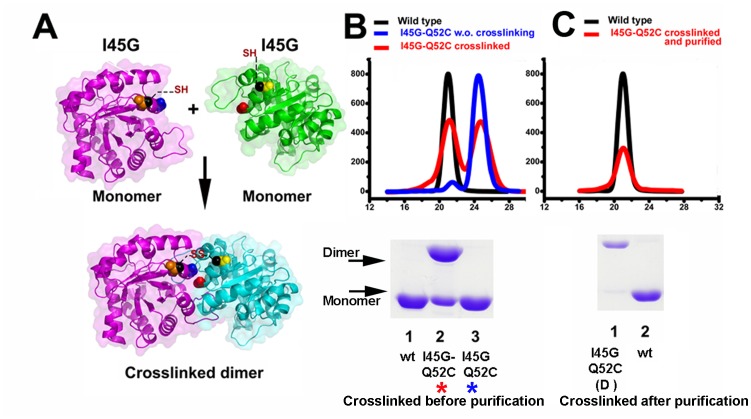
Fig 10. Disulfide Cross-linker induced dimerization of I45G mutant.
(A) Localization of the engineered I45G-Q52C double mutant. The upper panel represents the monomeric I45G-Q52C double mutatn that may assemble as a dimer by effect of a cross-linking reaction (lower panel) (B) Gel filtration elution profiles and SDS-PAGE analysis for wild-type and I45G-Q52C double mutant before and after cross-linking. Approximately two thirds of the I45G-Q52C double mutant cross-linked in to a dimer as assessed by SDS-PAGE (lane 3 bottom panel). The differences between the percentage of assembled dimer by SDS-PAGE and gel filtration may due to a differential in the exposure of aromatic residues between the monomer and dimer (C) Gel filtration elution profiles and SDS-PAGE for wild-type and purified cross-linked I45G-Q52C double mutant. The gel filtration step efficiently separates the cross-linked I45G-Q52C double mutant from the unreacted protein (lane 1 bottom panel). The elution profiles have been normalized to ease comparison.