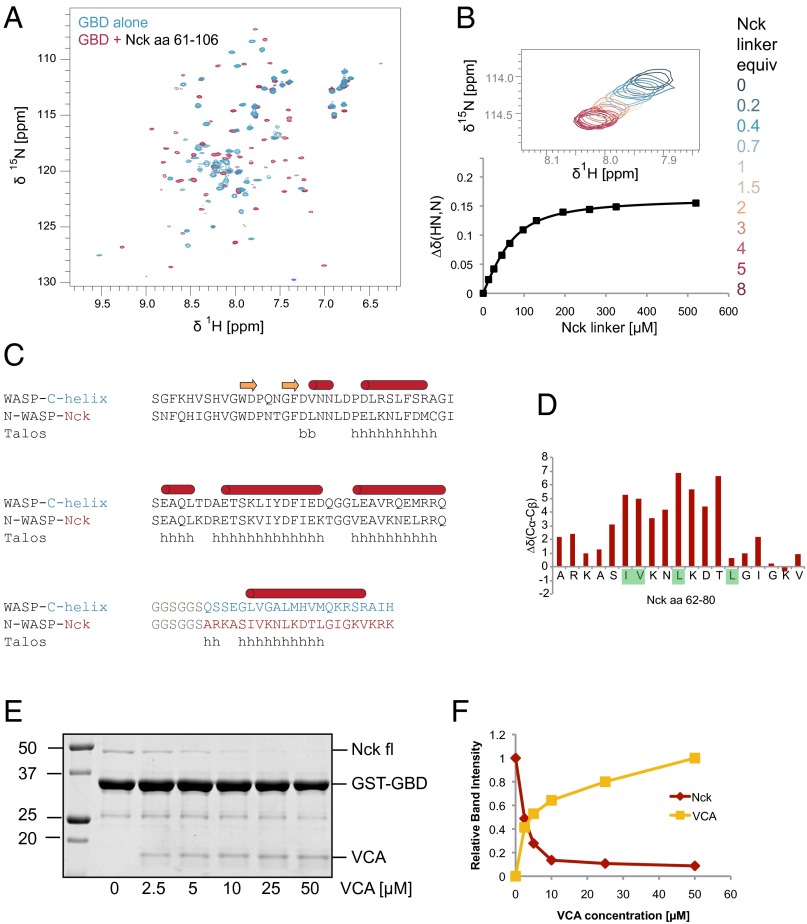
Fig. 5.
NMR analysis reveals direct binding of the Nck inter-SH3 linker and the N-WASP GBD. (A) [15N, 1H]-heteronuclear single-quantum coherence (HSQC) NMR spectra of 15N-labeled N-WASP GBD acquired in the presence and absence of unlabeled Nck linker peptide (amino acids 61–106). (B) NMR titration of 15N-labeled GBD (65 μM) with the Nck linker peptide. Chemical shift changes, along with the corresponding curve fit, are shown for a representative peak from the [15N, 1H]-HSQC spectrum. A binding Kd of 33 ± 8 μM was determined by fitting titration curves to a total of 17 peaks. (C) Sequence alignment of a WASP-GBD C-helix construct (10) and the N-WASP GBD Nck linker fusion protein. The secondary structure of the WASP–C helix complex (1EJ5.pdb) is indicated. (D) Secondary structure prediction of the N-WASP Nck fusion protein by Talos+ is shown. (E) Coomassie-stained gel from a competition pull-down experiment (bound fraction). N-WASP GST-GBD was used to pull down Nck in the presence of increasing N-WASP VCA. (F) Integrated band intensities from the Coomassie-stained gel showing Nck and VCA bound to GST-GBD.