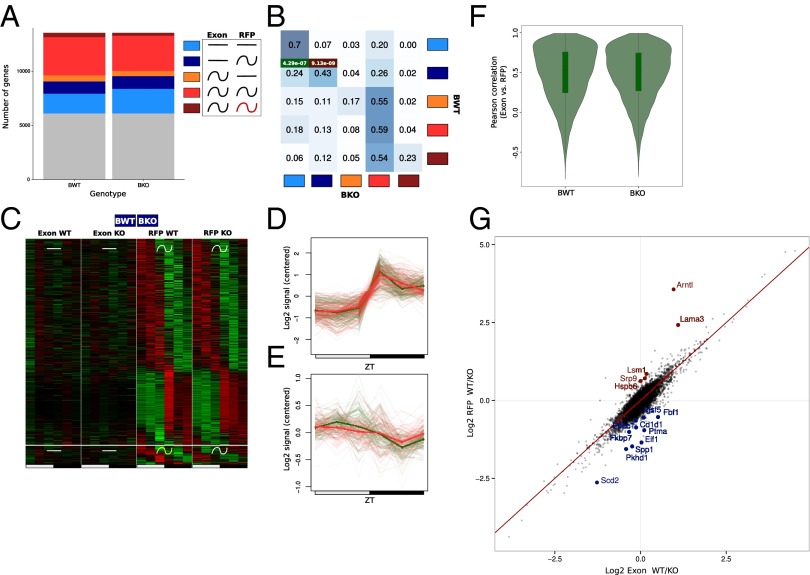
Fig. 6.
Bmal1 deletion affects translation efficiency in a constrained group of genes. The rhythmic analysis used is the same as for Fig. 3. (A) Gray, genes not assigned in any group; light blue, constant mRNA and RFP levels; dark blue, constant mRNA and rhythmic RFP; orange, rhythmic mRNA and constant RFP; red, rhythmic mRNA and RFP; brown, rhythmic mRNA and RFP with different rhythmic parameters. (B) Fraction of genes belonging in one of the five clusters in KO compared with WT mice. Intensity of the blue color in each box represents the conservation degree of behavior of the genes between WT and KO, with darkest blue corresponding to higher conservation. Hypergeometric test for TOP and TISU enrichment in the different cluster is applied. P values for the best enrichments are displayed in green and red for TISU and TOP motifs, respectively. (C) Heat map of the exonic and RFP signal for genes harboring a constant exonic and rhythmic RFP signal in WT and KO mice. (Top) Rhythmic parameters of RFP signals are shared between WT and KO mice. (Bottom) Rhythmic parameters of RFP signals are different between WT and KO mice. (D) Mean of relative RFP profiles across genes with TOP motifs in C with phase between ZT15–20 in WT (red) and KO (green) mice. Individual genes are shown as thin lines. (E) Mean of relative RFP profiles across genes with TISU motifs in C with phase between ZT4–10 in WT (red) and KO (green) mice. Individual genes are shown as thin lines. (F) Pearson correlation between RFP and fragmented exon RNA-Seq in WT and KO test. Translation is mainly dictated by mRNA pattern in WT and KO. (G) Log2 ratio of RFP and fragmented exonic RNA-Seq signals (UMR) between WT and KO mice, taken as a measure of (relative) translation efficiency. Genes showing a significantly (false discovery rate ≤0.05) increased (logFC < −0.5) or decreased (logFC > 0.5) in translation efficiency in KO mice are colored in blue and red, respectively.