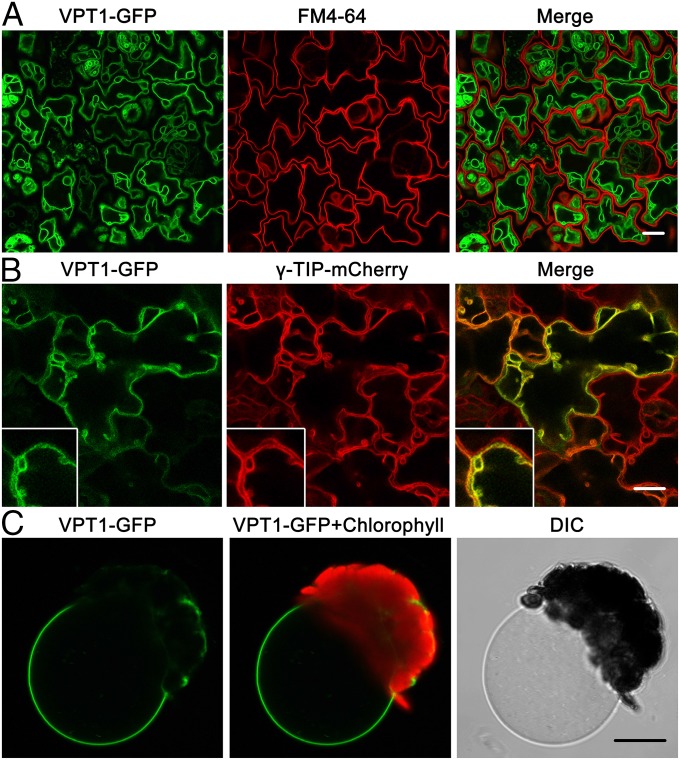
Fig. 4.
Subcellular localization of VPT1-GFP in the vacuole membrane. (A) Confocal microscopy of GFP signals in the epidermal cells from a cotyledon of a 3-d-old transgenic vpt1 seedling expressing 35S:VPT1-GFP. The panels, from left to right, show the GFP signals (green), the plasma membrane fluorescence stained with FM4-64 (red), and an overlay (of green and red) from the same sample. (Scale bar: 10 μm.) (B) VPT1-GFP signal overlaid with a γ-TIP-mCherry signal in the epidermal cells from a cotyledon of a 5-d-old seedling expressing 35S:VPT1-GFP and 35S:γ-TIP-mCherry. The panels, from left to right, show the GFP signals (green), the mCherry signals (red), and an overlay (of green and red) from the same sample. TIP (a tonoplast intrinsic protein) is a tonoplast marker (21). (Inset) The intermembrane space and sag area pressed by nuclei or plastids (21). (C) A vacuole released from a mesophyll protoplast isolated from transgenic plants expressing VPT1-GFP. (Scale bar: 10 μm.)