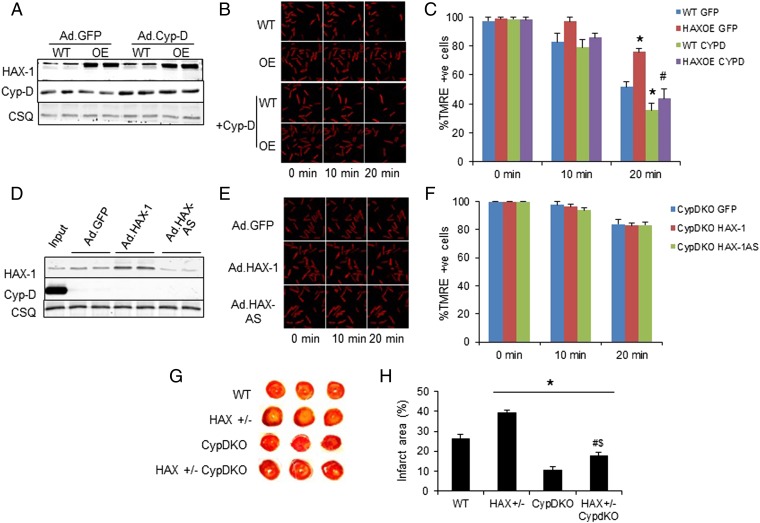
Fig. 4.
The effects of HAX-1 are mainly mediated by cyclophilin-D. (A) Cyp-D expression was increased to similar levels in WT and HAX-OE cells after adenoviral infection of adult rat cardiomyocytes. (B and C) Adenoviral delivery of Cyp-D removed the protection mediated by HAX-1 overexpression upon 2 mM hydrogen peroxide administration. CSQ was used as a loading control. n = 4–6 hearts (>12 cells per heart); *P < 0.05 vs. WT GFP at 2 min; #P < 0.05 vs. HAX-OE GFP at 20 min. (D) HAX-1 levels after adenoviral delivery of Ad.GFP, Ad.HAX-1, and Ad.HAX-AS in CypD-KO cells. WT cardiac homogenate was loaded to serve as input. (E and F) Cyp-D ablation abolished the effect of different HAX-1 levels on the maintenance of mitochondrial membrane potential upon 2 mM hydrogen peroxide challenge. CSQ was used as a loading control. n = 4–5 hearts (>16 cells per heart). (G and H) Cyp-D ablation significantly reduced infarct size in HAX-1 heterozygous knockout hearts. n = 4 for each group; *P < 0.05 vs. WT; #P < 0.05 vs. HAX+/−; $P < 0.05 vs. CypD-KO. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM.