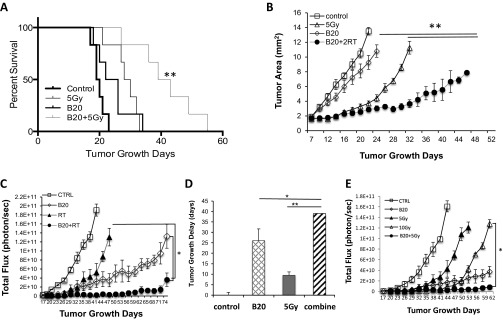
Fig. S3.
Combination therapy more effectively inhibits tumor growth of HEI-193 schwannomas in both intracranial and sciatic nerve models. Kaplan–Meier survival curve (A) and tumor growth (B) curve of mice in HEI193 intracranial model. Tumor growth from untreated (control), B20 treated (B20), radiated (5 Gy), and B20 and RT combination groups were measured by OFDI every 3 days (n = 8). **P < 0.01 compared with B20 and radiation monotherapies. Tumor growth curves (C) and tumor growth delay (D) of HEI193 tumor implanted under the nerve sheath of sciatic nerve in nude mice. Tumor growth was measured every 3 d by whole body imaging (WBI, n = 8). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 compared with B20 and radiation monotherapies. (E) Tumor growth in untreated (control), B20 treated (B20), low-dose radiation (5 Gy), high-dose radiation (10 Gy), and B20 combined with low-dose radiation (5 Gy) were measured by WBI (n = 8). *P < 0.05 compared with 10 Gy. Representative of at least three independent experiments, all data presented are mean ± SEM.