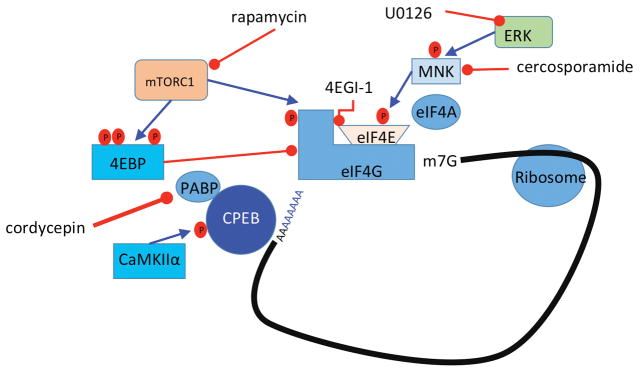
Figure 2. Translational control pathways involved in hyperalgesic priming.
mTORC1 phosphorylates 4EBPs, negative regulators of eIF4F formation. This results in its dissociation from eIF4E, allowing the binding of eIF4E to eIF4G. Phosphorylation of eIF4E (via ERK/MNK1/2) or eIF4G (via mTORC1) enhances the formation of the eIF4F complex, promoting translation. Phosphorylation of CPEB by CamKIIα enhances translation efficiency by increasing the length of the poly A tail in mRNAs containing a CPE sequence. Taken together, eIF4F complex formation enhances cap-dependent translation, which is necessary for the induction of priming via translational control of gene expression in sensory afferents.