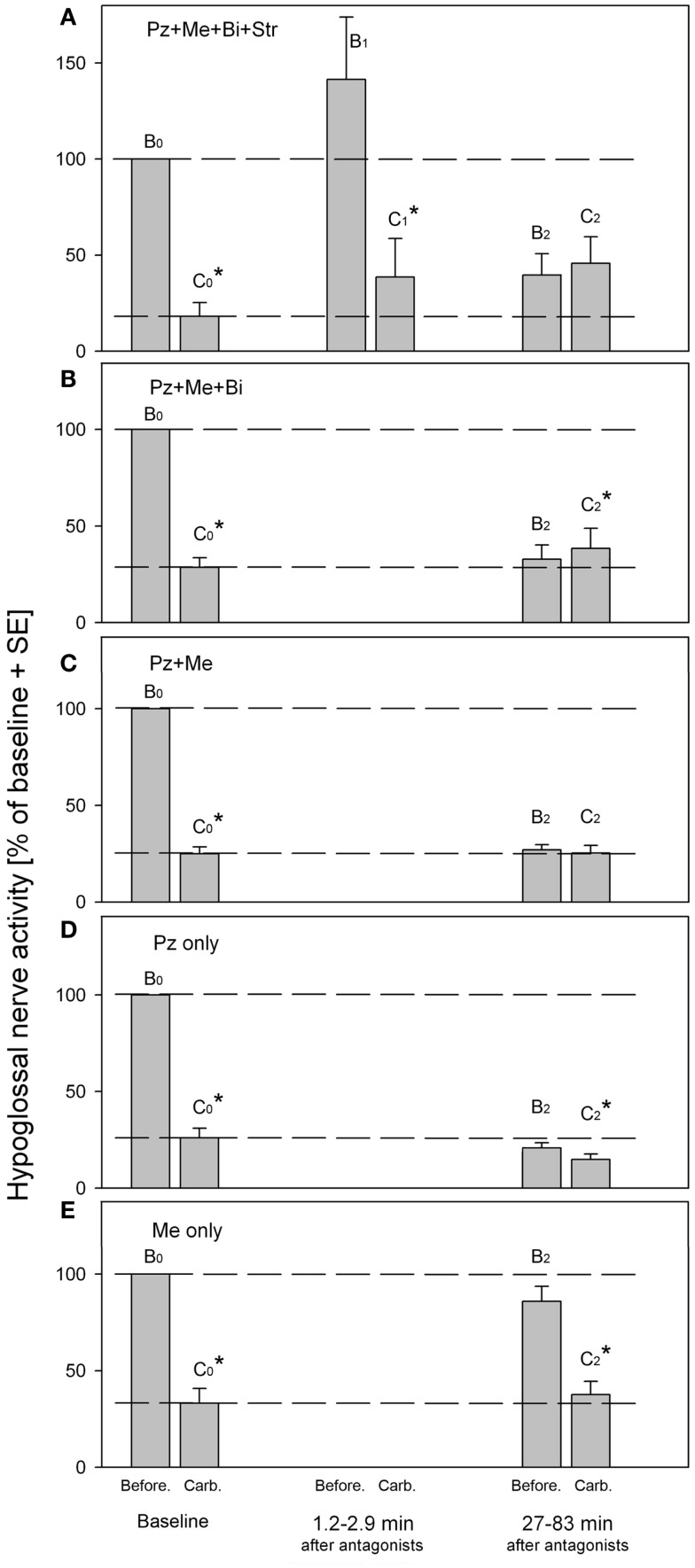
Figure 2.
Summary of hypoglossal nerve activity during carbachol- induced REM sleep-like episodes that were evoked before (baseline B0,C0) and at different times after (B1,C1 and B2,C2), the injections of the antagonist combinations into hypoglossal nucleus. (A) Combined injections of prazosin, methysergide, bicuculline and strychnine. (B) Combined injections of prazosin, methysergide and bicuculline. (C) Combined injections of prazosin and methysergide. (D) Injections of prazosin only. (E) Injections of methysergide only. Pz, prazosin, an α1-adrenoceptor antagonist; Me, methysergide, a broad-spectrum serotonergic antagonist; Bi, bicuculline, a GABAA antagonist; Str, strychnine, a glycinergic antagonist. B0 and C0, baseline hypoglossal nerve activity measured before and during carbachol, respectively; B1 and C1, hypoglossal nerve activity during “early” carbachol responses; B2 and C2, hypoglossal nerve activity during “late” carbachol responses. *p < 0.05, paired t-test [adapted from Fenik et al. (33–35)].