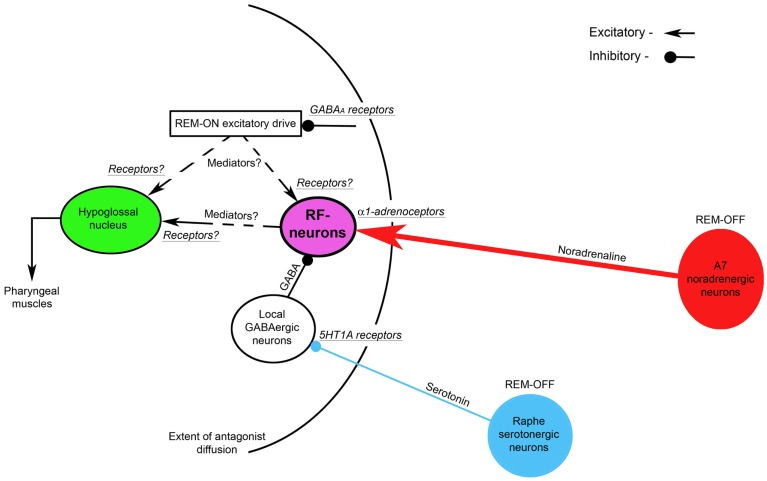
Figure 4.
A hypothetical brainstem circuit that illustrates the key neuronal pools, which participate in the state-dependent control of hypoglossal motoneuron excitability during REM sleep. The reticular formation neurons (RF-neurons) integrate and mediate noradrenergic and serotonergic drives to hypoglossal motoneurons. The REM-OFF A7 noradrenergic neurons excite RF-neurons via α1-adrenoceptors. The RF-neurons are tonically inhibited by local GABAergic neurons, activity of which is controlled by REM-OFF raphe serotonergic neurons via inhibitory 5HT1 receptors. The mediators and receptors through which RF-neurons directly or indirectly excite hypoglossal motoneurons remain to be determined. A hypothetical REM-ON excitatory drives to hypoglossal and/or RF-neurons are controlled by GABAA inhibitory receptors. The curved line shows the extent of the diffusion of antagonists that were injected into hypoglossal nucleus as discussed in this review.