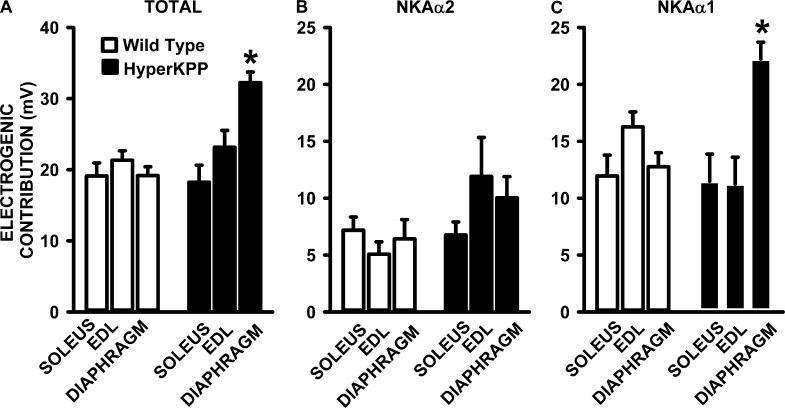
Figure 10.
The NKA electrogenic contribution at 4.7 mM K+ was significantly greater in the HyperKPP diaphragm than in the EDL and soleus. (A) Total NKA electrogenic contribution calculated from the difference in resting EM in the absence and presence of 100 µM ouabain, which fully inhibits NKAα1 and NKAα2 activity. (B) NKAα2 electrogenic contribution calculated from the difference in resting EM in the absence and presence of 1 µM ouabain, which reduced the activity of NKAα2 by 92% and that of NKAα1 by 6%. (C) NKAα1 electrogenic contribution calculated from the difference in total and NKAα2 electrogenic contribution. Error bars represent the SEM for the number of fibers and muscles given in Fig. 8. *, mean electrogenic contribution in HyperKPP was significantly different from the mean value for wild type; ANOVA and LSD; P < 0.05.