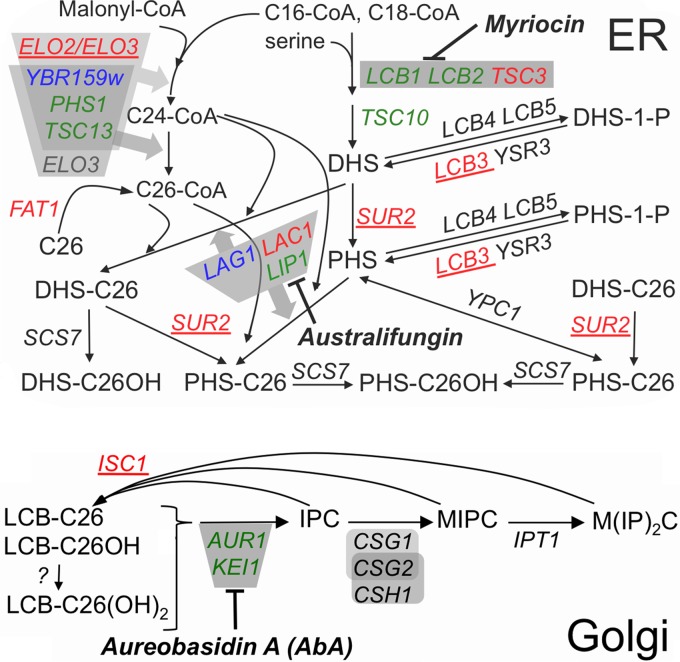
FIG 1.
Major pathways of sphingolipid biosynthesis in yeast. Gene names are in italic, essential genes are in green, activities dependent on protein complexes are in gray, and enzyme inhibitors are in bold italic. A detailed description of the biosynthetic reactions can be found in recent reviews (58, 67). Deletions of red and blue genes are predicted or known to reduce ceramide levels; those that scored as suppressors of the growth defect of strains with repressed AUR1 transcription are in red, and those which did not score, although present in the deletion library, are in blue. Deletions in the 5 underlined genes also were identified as suppressors in preliminary screens and were confirmed in serial dilution plating assays (Table 2). Long-chain bases (LCBs) of ceramides are dihydrosphingosine (DHS) or phytosphingosine (PHS); fatty acids of ceramides are indicated by the number of C atoms (e.g., C26) and their hydroxyl (OH) groups.