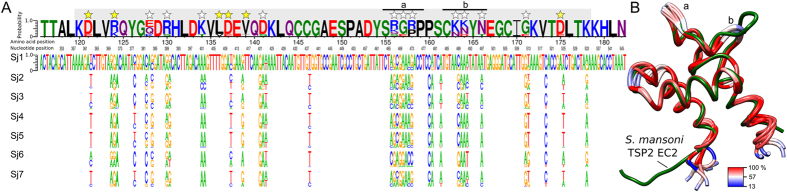
Figure 3. Sequence variability in the extracellular 2 domain (EC2) of the Schistosoma japonicum tetraspanin 2 ortholog (Sj-TSP2) among seven distinct populations.
(A) Nucleotide logos represent the frequency of base calls for each population in sites containing single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs). Amino acid logos representing the consensus sequence for all seven populations. SNPs leading to a similar (yellow star) or distinct (white star) change of the translated amino acid are indicated. Each amino acid logo is coloured according to its chemical characteristics; polar residues (G, S, T, Y & C) are green, neutral (Q & N) are purple, basic (K, R & H) are blue, acidic (D & E) are red and hydrophobic (A, V, L, I, P, W, F & M) are black. The extracellular 2 (EC2) domain is highlighted in grey. (B) Comparison of consensus Sj-TSP2-EC2 structures, modelled using the resolved protein structure of Sm-TSP2-EC2 (labelled green; RCSB accession number: 2M7Z) and highlighting structural changes (a & b) in the head region associated with the consensus amino acid sequence composition of each S. japonicum isolate. Proteins structures (S. japonicum) are coloured by percentage amino acid conservation among consensus protein translations.