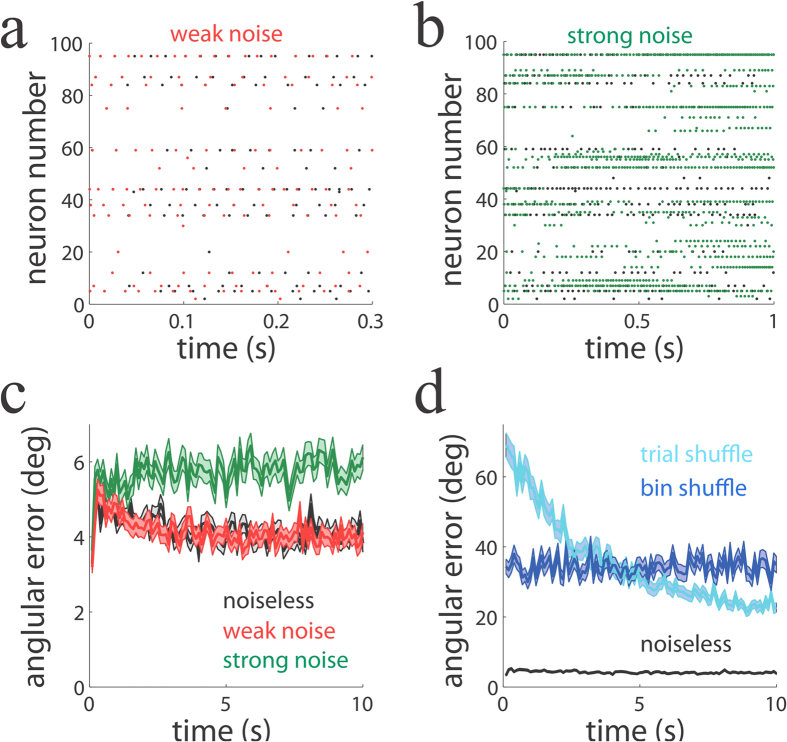
Figure 5. Slow firing rate covariations underlie reliable encoding.
(a,b) Population activity patterns over time for a noiseless (black dots), weak-noise (red) and strong-noise (green) network. The noiseless network is identical in the two panels but represented at two different time resolutions. Networks only differ in the injected noise variance, while other parameters including initial conditions are identical (Methods). (c) Angular error as a function of time for the three networks (100 ms time window). (d) Angular error as a function of time for the noiseless network (black line) and for trial- (light blue) and bin- (dark blue) shuffled networks. When the slow covariations of firing rate are destroyed by the shuffling, performance largely deteriorates compared to the one of the noiseless network.