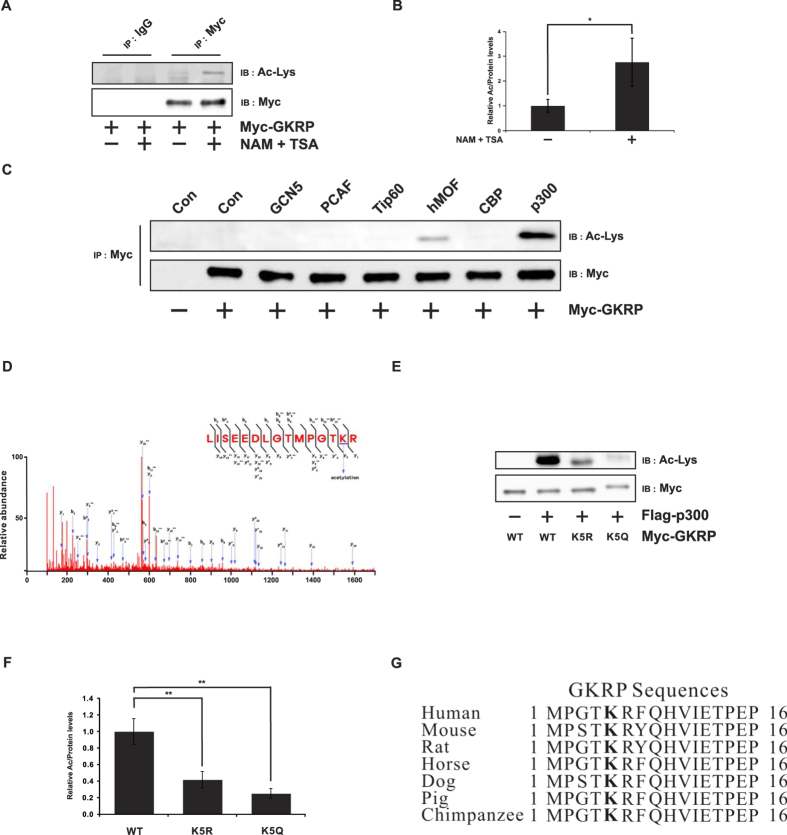
Figure 1. GKRP is acetylated by p300.
(A) Effects of histone deacetylase inhibitors on GKRP. HeLa cells transfected with Myc-tagged GKRP were treated with 5 mM NAM and 1 μM TSA 6 hr before harvest. (B) Band intensities of acetylated Myc-GKRP were quantified by Image J software. The values from samples not treated with NAM and TSA were set to 1.0. Data are shown as the means ± SEM of four independent experiments. (C) Identification of the acetyltransferase responsible for GKRP acetylation. Expression vectors of various acetyltransferases (ATs) were co-transfected with pSG-Myc GKRP into HeLa cells. The immunoprecipitates (from antibodies against the various ATs) were then subjected to immunoblot with antibodies against Ac-Lys or Myc. (D) LC-MS/MS spectrum of GKRP peptides showing that acetylation occurs at K5. (E) Effects of site-specific mutation on the potential acetylation site, GKRP K5. Substitutions of Lys (K) with Arg (R) or Glu (Q) at the indicated sites are shown in parenthesis. HeLa cells transfected with the indicated mutant or wild-type plasmids were lysed and immunoprecipitated by an anti-Myc antibody. Acetylated GKRP was detected by an anti-Ac-Lys antibody. (F) Sequence alignment of the GKRP region containing K5 from various species. NAM, nicotinamide; TSA, Trichostatin A. Data are expressed as means ± SEMs, n = 4, *p ≤ 0.05; **p ≤ 0.01.