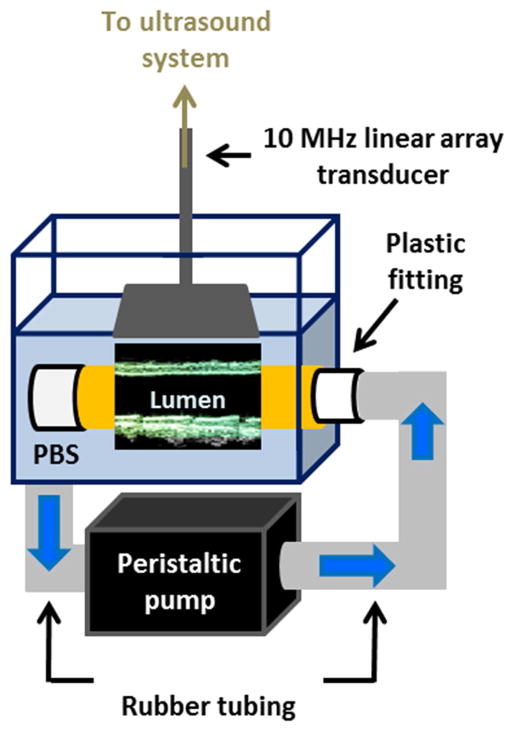
Figure 2.
Schematic of the setup used for ex vivo experiments. The canine aorta is held in place in a PBS-filled tank using plastic fittings. The peristaltic pump draws PBS from the tank, delivering pulsatile flow through the specimen and back into the bath. The imaged segment length was equal to the width of the field of view because the transducer was held in place parallel to the specimen as shown in Figure 2.