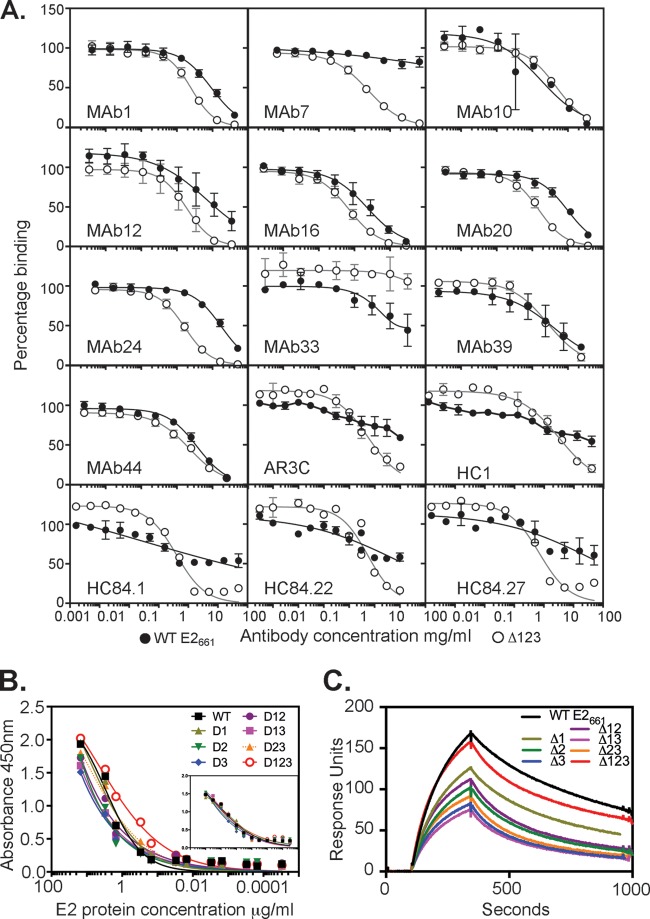
FIG 4.
Ability of MAbs to inhibit binding between E2661 or Δ123 and recombinant MBP-LEL113–201. (A) Serial dilutions of antibody were mixed with 50 ng E2 E2661 or Δ123 and applied to plates coated with purified dimeric MBP-LEL113–201. Bound E2 was detected with rabbit anti-His and horseradish peroxidase-labeled goat anti-rabbit IgG. Results shown are the means ± standard deviations of data from at least 2 independent experiments. Data were normalized to the percentage of E2 binding to CD81 in the absence of MAb. Curves were fitted with one-site-specific binding with the Hill slope equation in Prism v 6.0f. (B) Binding of E2661 proteins containing one or more variable region deletions to solid-phase MBP-LEL113–201. The inset graph shows the capture of E2 proteins with GNA-lectin and detection with anti-His antibody and confirms that similar amounts of E2 protein were present in every well. (C) Biosensor analysis of binding of E2661 and variants containing one or more variable region deletions to dimeric MBP-LEL113–201. Four concentrations of each E2661 protein were flowed over biosensor chips coated with MBP-LEL113–201, and the curves generated with 100 μg/ml E2 protein are shown.