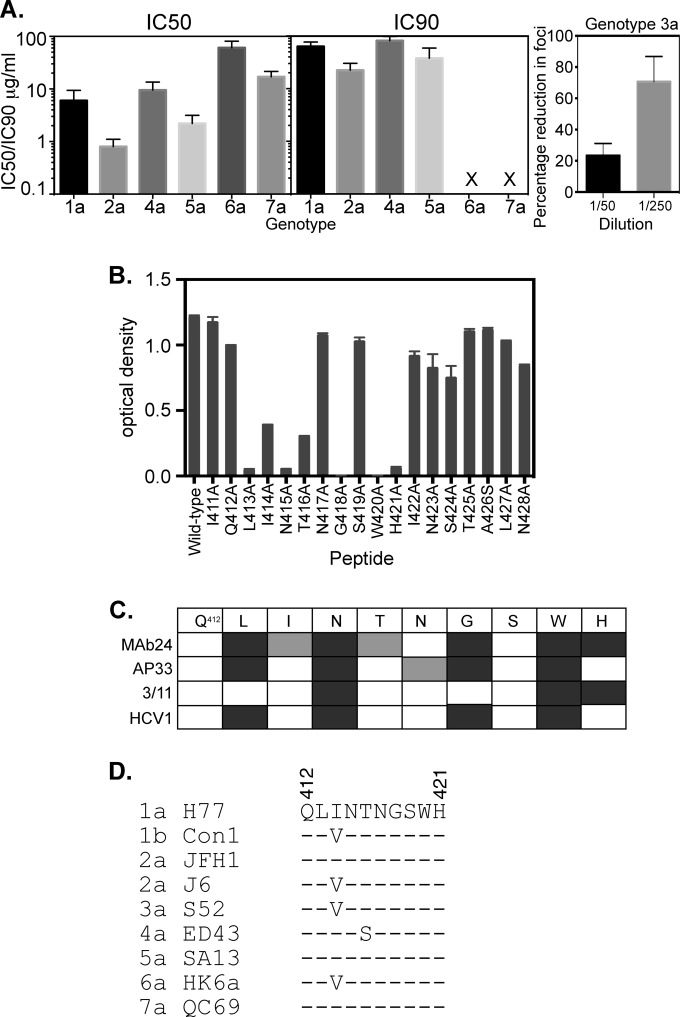
FIG 6.
Properties of MAb24. (A) Ability of MAb24 to mediate neutralization of different HCV genotypes. IC50s and IC90s (micrograms per milliliter) were derived from neutralization assays performed with HCVpp (genotype 1a) and HCVcc (genotypes 2a and 4a to 7a). X indicates that no neutralization was observed at the highest concentration of antibody tested. Data shown are the means ± standard errors of the means of data from at least three independent experiments. Genotype 3a neutralization was performed by incubating MAb24 with HCVcc and applying this mixture to Huh7.5 cells plated onto coverslips. Foci were visualized 3 days later after staining with anti-NS5A antibody and Alexa 488-labeled anti-mouse antibody. The mean percent reductions in foci on 2 coverslips relative to the no-antibody control and standard deviations are shown. Results are representative of data from two independent experiments. (B) Binding of MAb24 to the peptide spanning residues 411 to 428 with alanine substitutions at each position. Binding values are the means of data from duplicate samples ± standard deviations. (C) Comparison of the epitopes recognized by murine antibody AP33, rat antibody 3/11, and an antibody produced in transgenic mice containing human antibody genes, HCV1, for the region spanning residues 412 to 421. Mutations that abolish binding are shown in dark gray. Mutations that reduce binding are shown in light gray. (D) Alignment of the region spanning residues 412 to 421 in representative isolates of the 7 HCV genotypes.