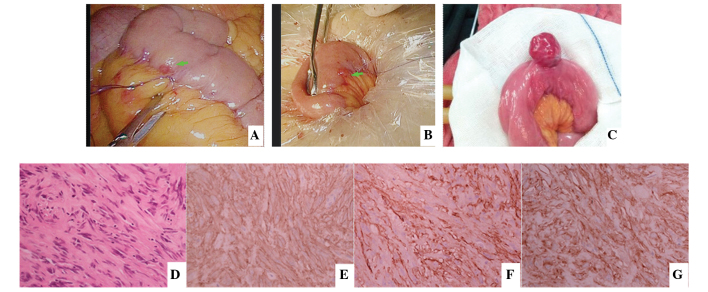
Figure 2.
(A and B) An abnormal lesion was detected in the small intestine of a patient during the process of laparoscopic rectal surgery and suturing was used to mark the lesion first. The small intestine was then removed from umbilical incision to remove the 0.3-cm lesion, which was the smallest GIST identified in the present study. The diagnosis was confirmed by post-operative pathology and immunohistochemistry. (C) Small intestine GIST found when detecting the small intestine in open surgery. (D) Hematoxylin and eosin staining revealed spindle cell in morphology and immunohistochemical analysis was performed for the detection of (E) CD117(+), (F) CD34(+) and (G) discovered on GIST-1(+). Excluding (C), all images were obtained from the same patient. GIST, gastrointestinal stromal tumor; CD, cluster of differentiation.