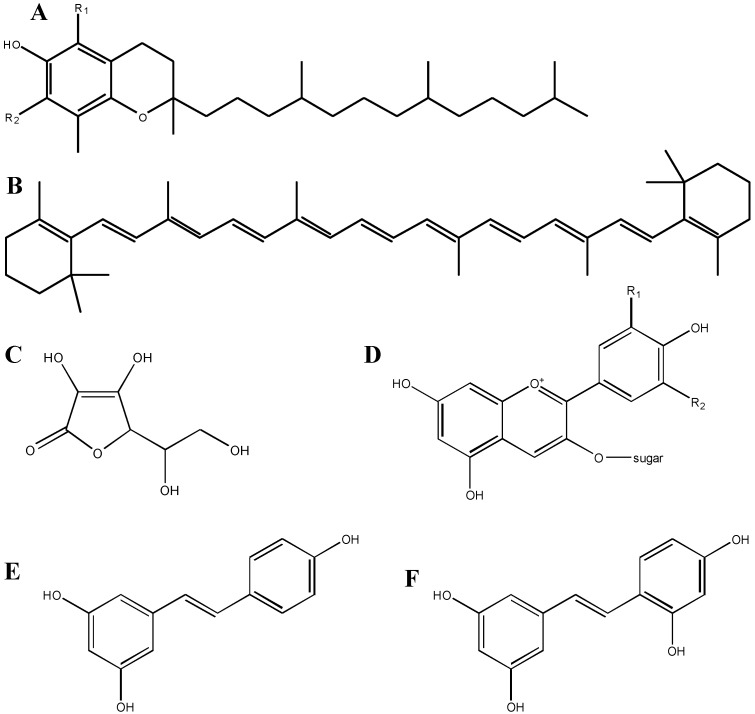
Figure 1.
Structures of various antioxidant compounds. A: vitamin E (tocopherol); constituents at the R1 and R2 positions are either –H or –CH3; B: beta-carotene, a member of the carotenoid family; C: vitamin C (ascorbic acid); D: anthocyanin; constituents at the R1 and R2 positions are –H, –OH or –OCH3, and the sugar is glucose, galactose or arabinose; E: resveratrol; F: oxyresveratrol; note the additional OH group as compared to resveratrol.