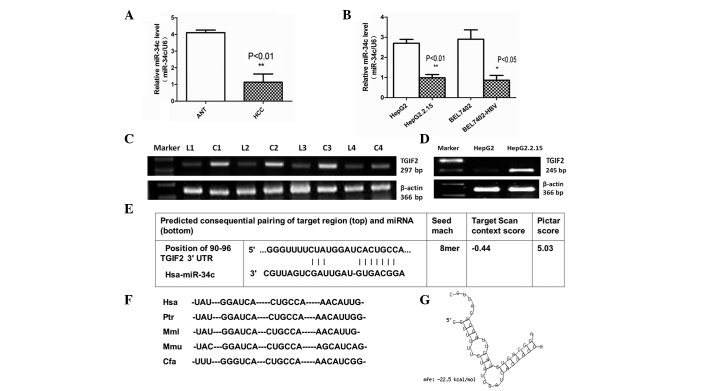
Figure 1.
miR-34c expression was downregulated in HBV-associated HCC, and TGIF2 is a putative target of miR-34c. (A) Expression levels of miR-34c were significantly reduced in HBV-associated HCC clinical specimens compared with ANT (**P<0.01). (B) Quantitative PCR results showed that the expression levels of miR-34c were reduced in HepG2.2.15 compared with HepG2 cells (**P<0.01), as well as in BEL7402-HBV compared with BEL7402 cells (*P<0.05). (C) mRNA expression levels of TGIF2 were significantly upregulated in HBV-associated HCC tissues compared with ANT. (D) Reverse transcription-PCR results showed that TGIF2 was upregulated in HepG2.2.15 compared with HepG2 cells. All of the above data were obtained from three independent experiments. (E) TGIF2 was identified as a potential target gene of miR-34c using TargetScan and PicTar software. (F) The TargetScan prediction showed a common binding sequence on the 3′-UTR of TGIF2 that was conserved across vertebrate species, including human, chimpanzee, rhesus macaque, mouse and dog. (G) The duplex structure of miR-34c and the 3′-UTR of TGIF2 is shown. The free energy of miR-34c bound to the target site of TGIF2 was calculated by RNAhybrid (minimum free energy, −22.5 kcal/mol). miR-34c, microRNA-34c; ANT, adjacent non-cancerous tissue; PCR, polymerase chain reaction; HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; HBV, hepatitis B virus; 3′-UTR, 3′-untranslated region; TGIF2, TGFB-induced factor homeobox 2.