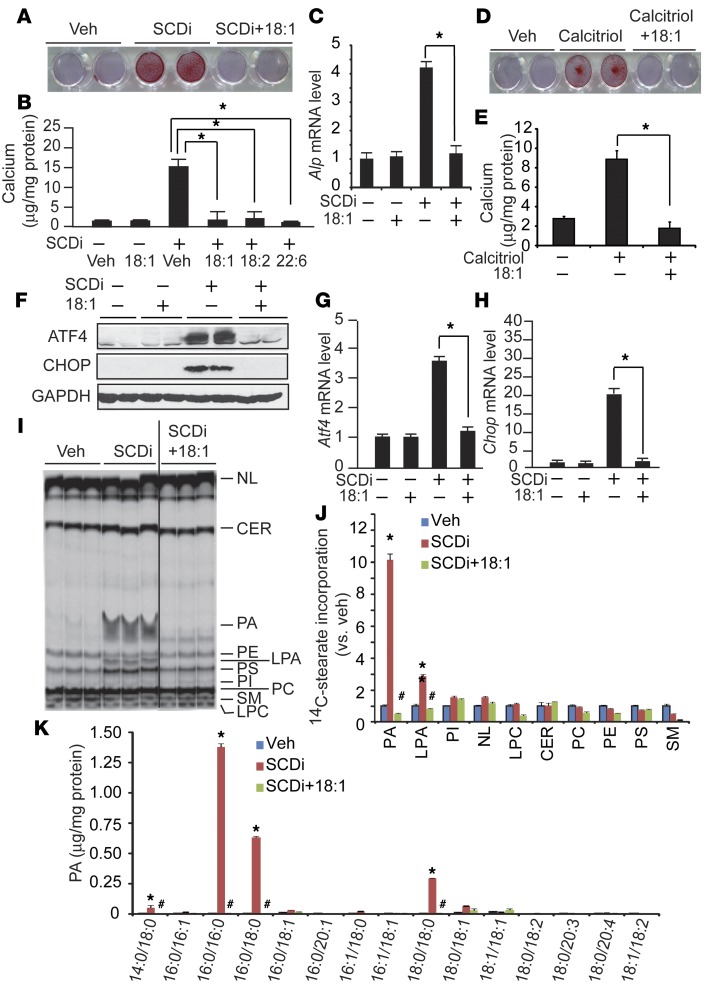
Figure 6. UFA cotreatment normalizes mineralization, osteogenic differentiation, ER stress, and PA accumulation.
(A–C) UFAs blocked SCDi-induced mineralization (A and B) and osteogenic differentiation (C) of VSMCs. Human VSMCs were treated with 200 μM UFAs in the presence of 300 nM SCDi for 7 days in the presence of 2.0 mM inorganic phosphate. (A) Seven days after the treatments, the cells were stained with Alizarin red to identify calcium deposits. (B) Calcium content was analyzed using a colorimetric assay. (C) Alp mRNA levels were analyzed by qPCR. (D and E) Calcitriol-induced mineralization is blocked by 18:1n-9 supplementation. Human VSMCs were treated with 100 nM calcitriol in the presence of 200 μM 18:1n-9 for 7 days. (F–H) UFAs such as 18:1n-9 completely blocked ER stress induced by SCDi. VSMCs were treated with SCDi acid for 24 hours. Total protein extracts were subjected to immunoblot analysis with ATF4- and CHOP-specific antibodies. Atf4 and Chop mRNA levels were quantified by qPCR. (I) Autoradiography and (J) quantification of 14C-18:0 incorporation into the lipid fraction. Human VSMCs were treated with 200 μM 18:1n-9 in the presence of 300 nM SCDi and 14C-18:0 (1 μCi). The black line in I indicates that the image was derived from noncontiguous lanes of the same plate. Lipids were separated on a boric acid–coated TLC. (K) Absolute levels of PA species in VSMCs cotreated with SCDi and 18:1n-9. Human VSMCs were treated with 200 μM 18:1n-9 in the presence of 300 nM SCDi for 24 hours. Each PA content was analyzed with LC-MS/MS. NL, neutral lipids. n = 4, *P < 0.01 vs. vehicle (Veh) and #P < 0.01 vs. SCDi (n = 3–6, one-way ANOVA).