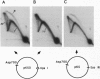
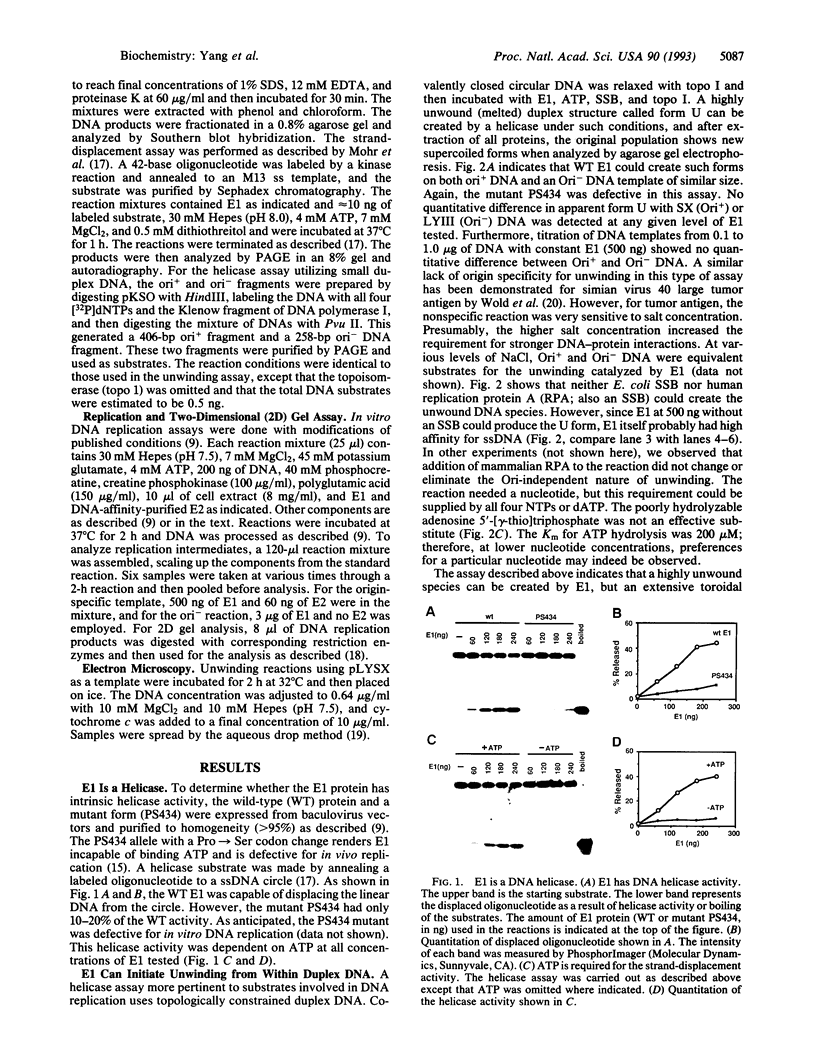
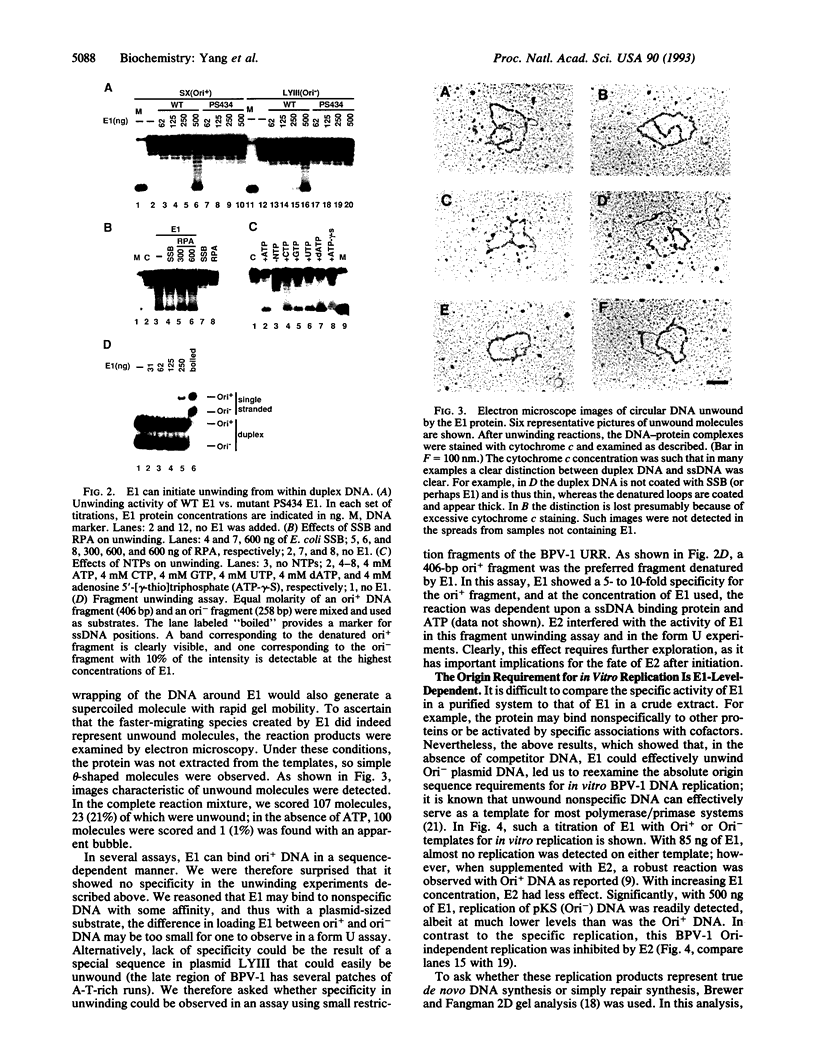
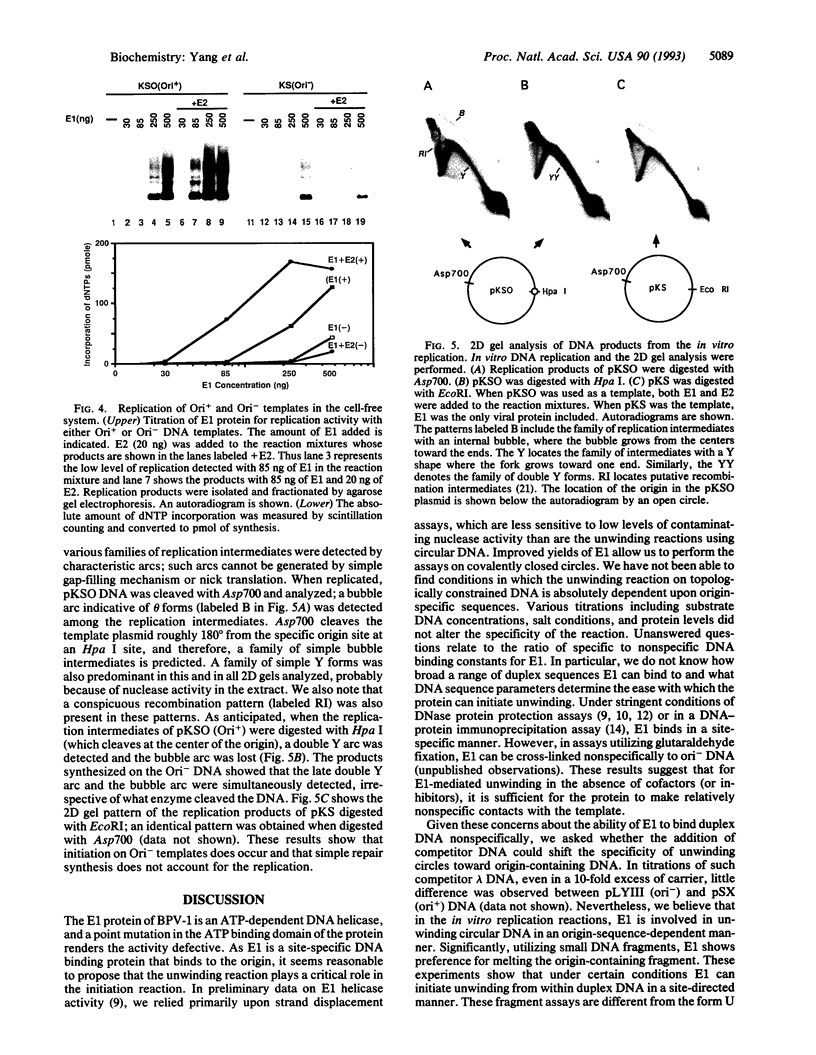
Abstract
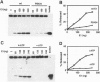
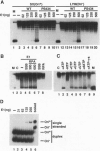
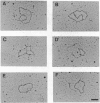
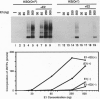
For efficient DNA replication of papillomaviruses, only two viral-encoded proteins, E1 and E2, are required. Other proteins and factors are provided by the host cell. E2 is an enhancer of both transcription and replication and is known to help E1 bind cooperatively to the origin of DNA replication. E1 is sufficient for replication in extracts prepared from permissive cells, but the activity is enhanced by E2. Here we show that purified E1 can act as an ATP-dependent DNA helicase. To measure this activity, we have used strand displacement, unwinding of topologically constrained DNA, denaturation of duplex fragments, and electron microscopy. The ability of E1 to unwind circular DNA is found to be independent of origin-specific viral DNA sequences under a variety of experimental conditions. In unfractionated cellular extracts, E1-dependent viral DNA replication is origin-dependent, but at elevated E1 concentrations, replication can occur on non-origin-containing DNA templates. This conversion from an origin-dependent replication system to a nonspecific initiator system is discussed in the context of the current understanding of the initiation of chromosomal DNA replication.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Borowiec J. A., Dean F. B., Bullock P. A., Hurwitz J. Binding and unwinding--how T antigen engages the SV40 origin of DNA replication. Cell. 1990 Jan 26;60(2):181–184. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90730-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruckner R. C., Crute J. J., Dodson M. S., Lehman I. R. The herpes simplex virus 1 origin binding protein: a DNA helicase. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 5;266(4):2669–2674. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnett S., Zabielski J., Moreno-Lopez J., Pettersson U. Evidence for multiple vegetative DNA replication origins and alternative replication mechanisms of bovine papillomavirus type 1. J Mol Biol. 1989 Mar 5;206(1):239–244. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90537-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiang C. M., Ustav M., Stenlund A., Ho T. F., Broker T. R., Chow L. T. Viral E1 and E2 proteins support replication of homologous and heterologous papillomaviral origins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 1;89(13):5799–5803. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.13.5799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Del Vecchio A. M., Romanczuk H., Howley P. M., Baker C. C. Transient replication of human papillomavirus DNAs. J Virol. 1992 Oct;66(10):5949–5958. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.10.5949-5958.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fierer D. S., Challberg M. D. Purification and characterization of UL9, the herpes simplex virus type 1 origin-binding protein. J Virol. 1992 Jul;66(7):3986–3995. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.7.3986-3995.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilley D., Preer J. R., Jr, Aufderheide K. J., Polisky B. Autonomous replication and addition of telomerelike sequences to DNA microinjected into Paramecium tetraurelia macronuclei. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;8(11):4765–4772. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.11.4765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krysan P. J., Calos M. P. Replication initiates at multiple locations on an autonomously replicating plasmid in human cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;11(3):1464–1472. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.3.1464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matson S. W., Kaiser-Rogers K. A. DNA helicases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:289–329. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.001445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mello C. C., Kramer J. M., Stinchcomb D., Ambros V. Efficient gene transfer in C.elegans: extrachromosomal maintenance and integration of transforming sequences. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(12):3959–3970. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04966.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohr I. J., Gluzman Y., Fairman M. P., Strauss M., McVey D., Stillman B., Gerard R. D. Production of simian virus 40 large tumor antigen in bacteria: altered DNA-binding specificity and dna-replication activity of underphosphorylated large tumor antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6479–6483. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Méchali M., Kearsey S. Lack of specific sequence requirement for DNA replication in Xenopus eggs compared with high sequence specificity in yeast. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):55–64. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90526-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun S., Thorner L., Lentz M., MacPherson P., Botchan M. Identification of a 68-kilodalton nuclear ATP-binding phosphoprotein encoded by bovine papillomavirus type 1. J Virol. 1990 Oct;64(10):5093–5105. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.10.5093-5105.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thresher R., Griffith J. Electron microscopic visualization of DNA and DNA-protein complexes as adjunct to biochemical studies. Methods Enzymol. 1992;211:481–490. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(92)11026-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsurimoto T., Melendy T., Stillman B. Sequential initiation of lagging and leading strand synthesis by two different polymerase complexes at the SV40 DNA replication origin. Nature. 1990 Aug 9;346(6284):534–539. doi: 10.1038/346534a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ustav M., Ustav E., Szymanski P., Stenlund A. Identification of the origin of replication of bovine papillomavirus and characterization of the viral origin recognition factor E1. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(13):4321–4329. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb05010.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahle E., Lasken R. S., Kornberg A. The dnaB-dnaC replication protein complex of Escherichia coli. II. Role of the complex in mobilizing dnaB functions. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 15;264(5):2469–2475. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg D. H., Collins K. L., Simancek P., Russo A., Wold M. S., Virshup D. M., Kelly T. J. Reconstitution of simian virus 40 DNA replication with purified proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(22):8692–8696. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.22.8692. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson V. G., Ludes-Meyers J. A bovine papillomavirus E1-related protein binds specifically to bovine papillomavirus DNA. J Virol. 1991 Oct;65(10):5314–5322. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.10.5314-5322.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wold M. S., Li J. J., Kelly T. J. Initiation of simian virus 40 DNA replication in vitro: large-tumor-antigen- and origin-dependent unwinding of the template. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(11):3643–3647. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.11.3643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang L., Li R., Mohr I. J., Clark R., Botchan M. R. Activation of BPV-1 replication in vitro by the transcription factor E2. Nature. 1991 Oct 17;353(6345):628–632. doi: 10.1038/353628a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang L., Mohr I., Li R., Nottoli T., Sun S., Botchan M. Transcription factor E2 regulates BPV-1 DNA replication in vitro by direct protein-protein interaction. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1991;56:335–346. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1991.056.01.040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]