Fig. 4.
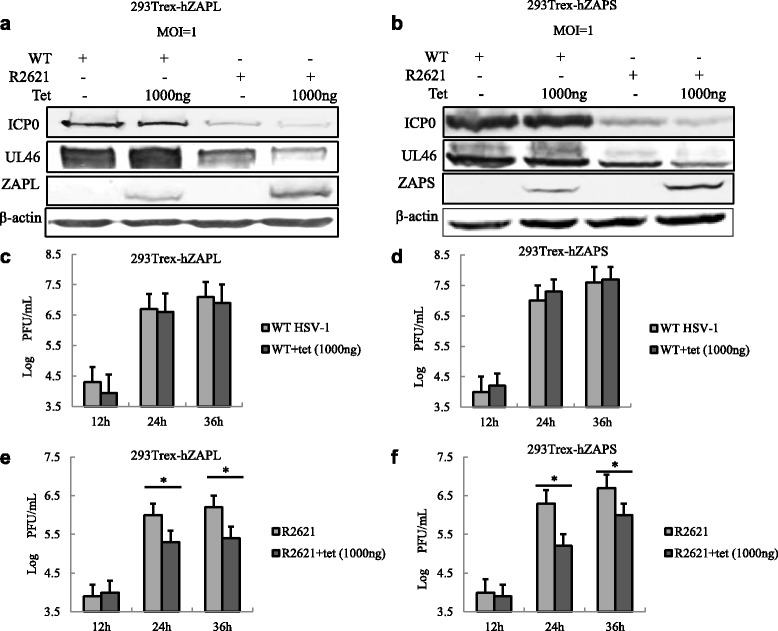
Expression of hZAP inhibits UL41-null mutant HSV-1 R2621 infection. a and b 293Trex-hZAPL cells or 293Trex-hZAPS cells were infected with WT HSV-1 or R2621 at an MOI of 1, respectively. At 2 h post-infection, cells were mock treated or treated with tetracycline (1000 ng/mL). At 36 h post-infection, cells were lysed and subjected to WB analysis with the indicated Ab. c and d 293Trex-hZAPL cells or 293Trex-hZAPS cells were infected with WT HSV-1. After 2 h post-infection, cells were treated with or without Tet (1000 ng/mL) to induce hZAPL or hZAPS expression. Viral growth curves were generated by traditional plaque assays at the indicated time points. e and f 293Trex-hZAPL cells or 293Trex-hZAPS cells were infected with R2621 virus. After 2 h post-infection, cells were treated with or without Tet (1000 ng/mL) to induce hZAPL or hZAPS expression. Viral growth curves were generated by traditional plaque assays at the indicated time points. One representative of three independent experiments was shown. (*P < 0.05)
