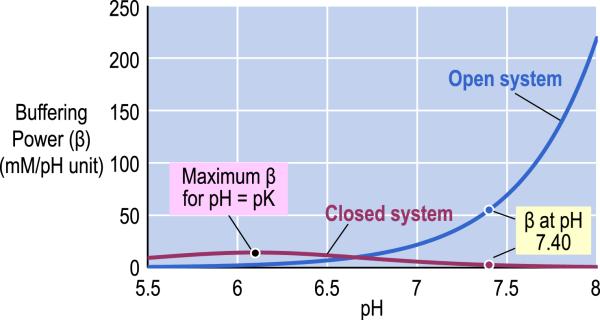
Fig. 1.
pH dependence of buffering power of the carbon dioxide/bicarbonate (CO2/HCO3−) buffer in a fluid having the composition of normal arterial blood. The blue line identifies the buffering power of the CO2/HCO3− buffer in a system that is “open” with respect to CO2 but closed to HCO3− . The purple line identifies the buffering power of the CO2/HCO3− buffer in a system that is “closed” with respect to both CO2 and HCO3− . For the calculations, we assumed that the pK of the CO2/HCO3− equilibrium is 6.1, [HCO3− ] is 24 mM, the solubility of CO2 is 0.03 mM/mm Hg, and PCO2 is 40 mm Hg. Modified from Fig. 28–4 in Medical Physiology, 2nd Edition Updated Edition, edited by WF Boron and EL Boulpaep, Philadelphia: Elsevier, 2012.